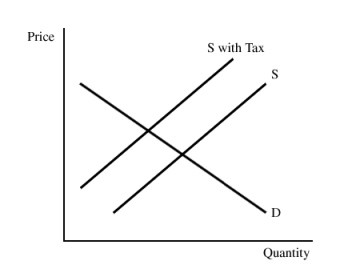
 The pollution tax in Figure 9.10:
The pollution tax in Figure 9.10:
A. increases equilibrium output.
B. decreases equilibrium price.
C. gives the firm an incentive to switch to a cleaner production process.
D. All of these
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The direct exchange of goods and services for other goods and services is known as
A) barter. B) purchasing power. C) intermediation. D) wholesale trade.
Suppose the domestic market demand function in a certain market where Q is measured in thousands of units is Qd = 20 - 2.5P, and the domestic market supply function is Qs = 2.5P - 7.5. Suppose further that the world price for the good in question is $3.40 per unit. Under conditions of free trade, how much producer surplus will there be?
A. $26,450 B. $200 C. $400 D. $600
Suppose you found $10,000 hidden under a rock and deposited it in a demand deposit account at your bank. If the reserve requirement was 20 percent, your deposit would initially add ____ to total demand deposits and over time increase the money supply by a maximum of ____
a. $2,000; $4,000 b. $2,000; $40,000 c. $10,000; $40,000 d. $10,000; $50,000
Regarding the purchasing of INSURANCE in particular, the most important difference(s) between "adverse selection" and "moral hazard" in general is/are that
A. adverse selection deals with "hidden information," whereas moral hazard deals with "hidden actions." B. usually the insurer worries more about adverse selection BEFORE the insurance is purchased, whereas it worries more about moral hazard AFTER the insurance is purchased. C. Both of the above statements are true. D. None of the above statements are true.