Giant and supergiant stars are rare because
a. they do not form as often as main sequence stars.
b. the star blows up before the giant or supergiant stage is reached
c. the giant or supergiant stage is very short.
d. the giant or supergaint stage is very long
C
You might also like to view...
Two planets travel in circular orbits about a star. The period of planet A is T, while that of planet B is 3T. What is the ratio of the orbital radii, 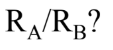
A. 0.33 B. 0.19 C. 0.48 D. 0.69
Why does the abundance of iridium suggest that the iridium came from an impact?
A. Iridium is rare on Earth's surface but common in meteorites that have impacted the Earth. B. Iridium forms in forest fires, which were presumably ignited by the impact. C. Iridium can only be made under the high-pressure conditions of an impact. D. Iridium does not exist on Earth, so it must have come from space.
Which direction do a comet's dust and plasma tails point?
A) straight behind the comet in its orbit B) generally away from the Sun C) perpendicular to the ecliptic plane D) always almost due north
The extent of the continental shelf, an underwater extension of continental crust from shoreline to basin, varies due to fluctuations in sea level. When sea level is lower, the continental shelf is
A) is narrow because less of the continental shelf is exposed. B) is narrow because less of the continental shelf is submerged. C) wider because some of the continental land would be submerged.