Which of the following conditions must hold in the equilibrium of a competitive market where the government puts a specific tax on consumers?
A) The quantity sold and the price paid by the buyer must lie on the demand curve.
B) The quantity sold and the seller's price must lie on the supply curve.
C) The quantity demanded must equal the quantity supplied.
D) the difference between the price the buyer pays and the price the seller receives must equal the specific tax.
E) all of the above
E
You might also like to view...
The figure above shows the U.S. supply of labor curve. What was the effect of the decline in birth rates during the 1960s and 1970s on the supply of labor curve in the 1980s?
A) a leftward shift of the supply of labor curve B) a rightward shift of the supply of labor curve C) a movement downward along the supply of labor curve from a point such as A to a point such as B D) The supply of labor curve became steeper. E) None of the above answers is correct because there was no change in the supply of labor curve.
Give several economic examples of how to test various joint linear hypotheses using matrix notation
Include specifications of R? = r where you test for (i) all coefficients other than the constant being zero, (ii) a subset of coefficients being zero, and (iii) equality of coefficients. Talk about the possible distributions involved in finding critical values for your hypotheses. What will be an ideal response?
The higher the HHI
A) the less dominated a market is by a single firm. B) the more competitive is the market. C) the more dominated a market is by a single firm. D) the less likely the Sherman Act will be applied to a firm.
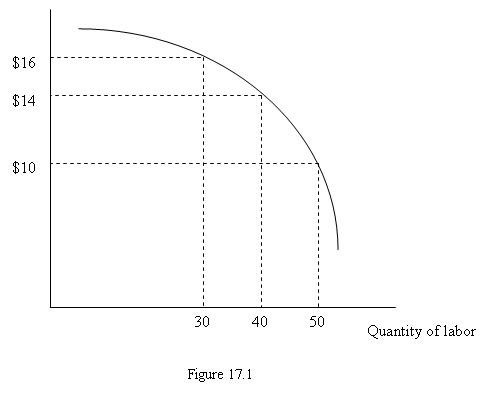 Figure 17.1 depicts a firm's marginal revenue product curve. If the product price increases, the marginal revenue product curve:
Figure 17.1 depicts a firm's marginal revenue product curve. If the product price increases, the marginal revenue product curve:
A. shifts downward. B. shifts upward. C. remains the same. D. None of these