The value of the momentum of a system is the same at a later time as at an earlier time if there are no
A. collisions between particles within the system.
B. inelastic collisions between particles within the system.
C. changes of momentum of individual particles within the system.
D. internal forces acting between particles within the system.
E. external forces acting on particles of the system.
Answer: E
You might also like to view...
Alcohols are distinguished by the fact that at least one hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon has been replaced by a(n)
a. carboxyl group. b. alkyl group. c. hydroxyl group. d. oxygen atom.
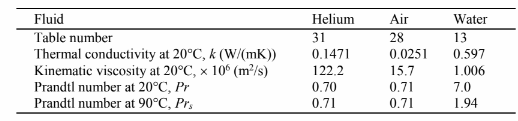
A platinum hot-wire anemometer operated in the constant-temperature mode has been used to measure the velocity of a helium stream. The wire diameter is 20 ?m, its length is 5 mm, and it is operated at 90°C. The electronic circuit used to maintain the wire temperature has a maximum power output of 5 watts and is unable to accurately control the wire temperature if the voltage applied to the wire is less than 0.5 volt. Compare the operation of the wire in the helium stream at 20°C and 10 m/s with operation in air and water at the same temperature and velocity. The electrical resistance of the platinum at 90°C is 21.6 ?? - cm.
GIVEN
• A constant temperature platinum hot-wire in a stream of helium
• Wire diameter = 20 ?m = 20 * 10–6 m
• Wire length (L) = 5 mm = 0.005 m
• Wire temperature (Tw) = 90°C
• Maximum electric power to wire (Pmax) = 5 W
• Minimum voltage (Vmin) = 0.5 V
• Helium temperature (T) = 20°C
• Helium velocity (U ) = 10 m/s
• Resistivity (re) = 21.6 ?? - cm.= 21.6 *10–8 ? - m FIND
• Compare the operation of the wire in helium to that in air and water
ASSUMPTIONS
• Radiation is negligible
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
John's mass is half the mass of Jill. They both start walking and John moves twice as fast as Jill. What is the ratio of the kinetic energy of Jill to the kinetic energy of John?
A) 4 B) 2 C) 1 D) 1/2 E) 1/8
Starburst galaxies
a. contain a large number of very young stars, but very little evidence of gas clouds. b. contain a large number of very old stars and almost no gas or dust. c. are often associated with a galaxy that is colliding with another galaxy. d. are common in rich clusters. e. are composed of filaments and voids.