When wages rise:
A. neither the opportunity cost of an hour of leisure nor the quantity of labor supplied is likely to change.
B. the opportunity cost of an hour of leisure declines.
C. the quantity of labor supplied always declines.
D. the opportunity cost of an hour of leisure increases.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a tax cut that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ and eventually to a long-run equilibrium at point ________, if left to self-correcting tendencies. 
A. D; C B. B; C C. B; A D. D; B
If Jason's fixed cost totals $400 with variable cost per unit of $10 at a quantity of 80 units, what would his average total cost at 80 units of output equal?
a. $10 b. $14 c. $15 d. $805
Ashley eats two bananas during a particular day. The marginal benefit she enjoys from eating the second banana
a. can be thought of as the total benefit Ashley enjoys by eating two bananas minus the total benefit she would have enjoyed by eating just the first banana. b. determines Ashley's marginal cost of the first and second bananas. c. does not depend on how many bananas Ashley has already eaten. d. cannot be determined unless we know how much she paid for the bananas.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 7.8 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 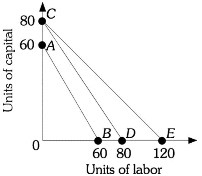 Figure 7.8Refer to Figure 7.8. The firm is currently along isocost CE. If the price of capital is $24, then the price of labor is
Figure 7.8Refer to Figure 7.8. The firm is currently along isocost CE. If the price of capital is $24, then the price of labor is
A. $16. B. $24. C. $80. D. $120.