Which of the following correctly describes a way in which deficit spending can impose a burden on future generations?
I.
Failure to allocate deficit spending to uses that boost future real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) will require taxing future generations at a higher rate to repay the resulting higher public debt.
II. Government deficits that lead to higher employment and real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in the future will generate increased income taxes for future governments, which will respond by spending the higher tax revenues, creating higher future government budget deficits.
III. Other things being equal, deficit spending fuels increased consumption of goods and services by the current generation that crowds out capital investment, thereby leaving future generations with a smaller stock of capital than otherwise would have existed.
A) I only B) II only C) I and III only D) II and III only
C
You might also like to view...
What is the "doom loop" responsible for the rapid development and severity of the 2009 euro crisis?
What will be an ideal response?
All else constant, an increase in the demand for bonds
A) increases the equilibrium quantity and the equilibrium price of bonds. B) increases the equilibrium quantity and decreases the equilibrium price of bonds. C) decreases the equilibrium quantity and increases the equilibrium price of bonds. D) decreases the equilibrium quantity and the equilibrium price of bonds.
How much revenue will the government raise each week from the tax?
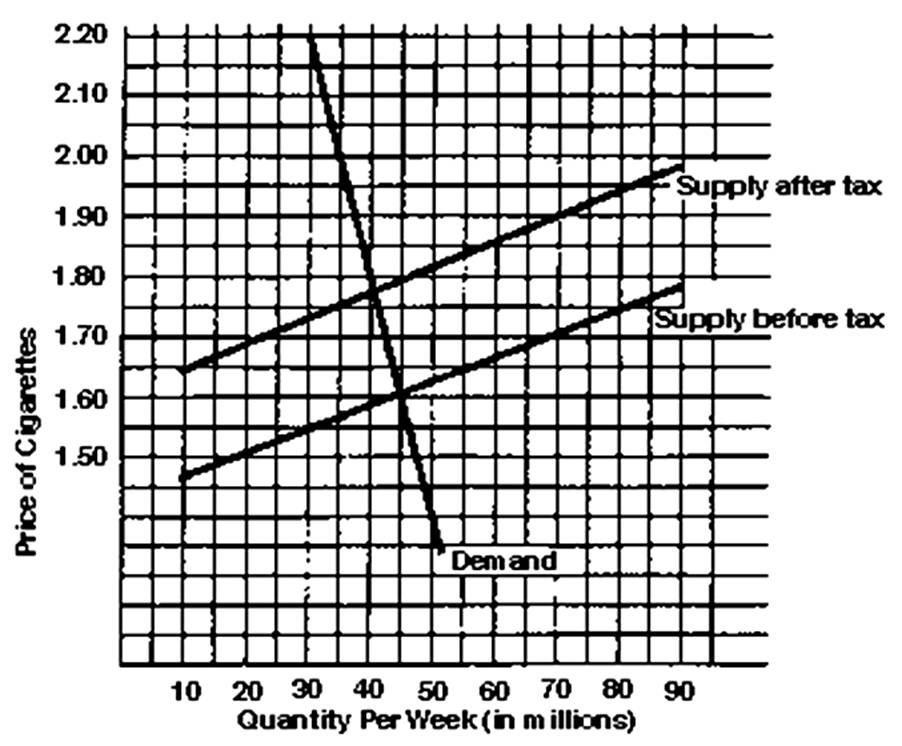
A. $8 million
B. $10 million
C. $20 million
D. $40 million
Hollywoodland, being self-sufficient in most products, trades only two goods with the Rest of the World (ROW), movies and automobiles. Both of these goods are produced using skilled labor (L) and capital (K) with the returns to capital being the interest rate (r) and the returns to skilled labor being the wage rate (w). The production of automobiles is capital intensive relative to the production of movies, and Hollywoodland is skilled-labor abundant relative to the ROW.a. State the Heckscher-Ohlin theorem and use it to predict the pattern of trade between Hollywoodland and the ROW.b. If the price of Hollywoodland's imports rises, while the price of its exports remain unchanged, what would happen to the factor returns in Hollywoodland in the long run? State the theorem used to explain
the answer, and briefly state the intuition behind the theorem. What will be an ideal response?