The per-worker production function in the Solow model assumes
A. constant returns to scale and increasing marginal productivity of capital.
B. constant returns to scale and diminishing marginal productivity of capital.
C. decreasing returns to scale and diminishing marginal productivity of capital.
D. increasing returns to scale and diminishing marginal productivity of capital.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Suppose the insurance company cannot tell them apart but expects them to be different values and charges them an average premium of $1850 . Who is more likely to buy this insurance?
a. Samantha b. Nadia c. Both of them d. None of them
Figure 9-2
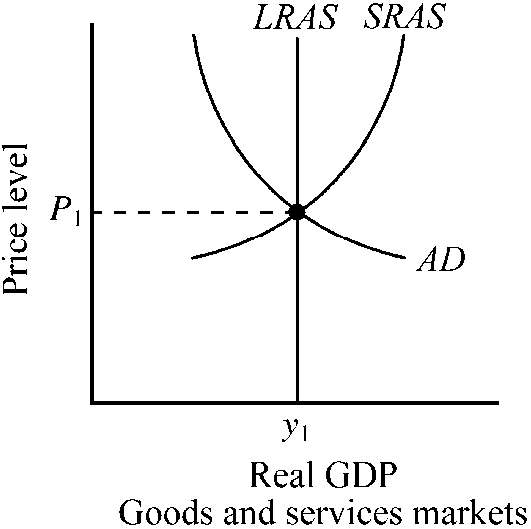
The output of the economy depicted in is
a.
equal to the full-employment output.
b.
greater than the full-employment output.
c.
less than the full-employment output.
d.
not sustainable in the long run.
Consider an incumbent that successfully links the pre-entry price and post-entry profit to prevent entry. The incumbent's monopoly profit is $10 million. If a rival successfully enters the market, the incumbent's profits will fall to $4 million. If the incumbent lowers output to 25,000 units, its rival will stay out of the market, resulting in an infinite stream of profits of $8 million annually. Due to a recent loan default, the current interest rate is whopping 210 percent. Is limit pricing profitable for the incumbent?
A. No since $4 million is less than $4.2 million. B. No, since $1.905 million is less than $2 million. C. Yes, since $19.05 million is greater than $2 million. D. Linking the pre-entry price to the post-entry profit is sufficient to guarantee the profitability of limit pricing.
Elastic demand displays considerable:
A. income stretch. B. cross-price stretch. C. price stretch. D. quantity stretch.