At the start of a cost-push inflation,
A) the price level rises and real GDP does not change.
B) the price level remains constant and real GDP increases.
C) the price level rises and real GDP decreases.
D) the price level remains constant and real GDP decreases.
E) the price level and real GDP both increase.
C
You might also like to view...
If you intend to begin jogging one week from today, and next week tell yourself you'll begin in another week, your preferences are:
A. revealed from your actions. B. more accurate in the future. C. irrational. D. time inconsistent.
The model: y* = 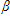
data-mathml="%3Cmath%20style%3D%22font%2Dfamily%3A%27Times%20New%20Roman%20Greek%27%22%20xmlns%3D%22http%3A%2F%2Fwww%2Ew3%2Eorg%2F1998%2FMath%2FMathML%22%3E%3Cmstyle%20mathsize%3D%2215px%22%3E%3Cmi%3E%26%23946%3B%3C%2Fmi%3E%3C%2Fmstyle%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E" src="@@PLUGINFILE@@/ppg__cognero__Ch_17_Limited_Dependent_Variable_Models_and_Sample_Selection_Correctons__media__46326d49-3bde-46dc-b6ef-4d50a0eeea1c.PNG" style="vertical-align:middle;" /> + u, given u|x ˜ Normal(0, 2) and y = max(0, y*) represents a:
A. ARCH model.
B. GARCH model
C. Tobit model
D. logit model
If the price level kept increasing, the short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve would get steeper because
A. the rate at which capacity can be expanded increases indefinitely. B. there are limits to how long workers can work long hours and capital can go without proper maintenance. C. all the unemployed would eventually be hired. D. the long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
In a duopoly, if one firm increases its price, then the other firm can:
A. Keep its price constant and thus increase its market share B. Keep its price constant and thus decrease its market share C. Increase its price and thus increase its market share D. Decrease its price and thus decrease its market share