The “free rider” problem occurs when a good is
A. not available.
B. not excludable.
C. not depletable.
D. not sold in free markets.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Refer to Table 4-10. An agricultural price floor is a price that the government guarantees farmers will receive for a particular crop. Suppose the federal government sets a price floor for wheat at $21 per bushel
a. What is the amount of shortage or surplus in the wheat market as result of the price floor? b. If the government agrees to purchase any surplus output at $21, how much will it cost the government? c. If the government buys all of the farmers' output at the floor price, how many bushels of wheat will it have to purchase and how much will it cost the government? d. Suppose the government buys up all of the farmers' output at the floor price and then sells the output to consumers at whatever price it can get. Under this scheme, what is the price at which the government will be able to sell off all of the output it had purchased from farmers? What is the revenue received from the government's sale? e. In this problem we have considered two government schemes: (1 ) a price floor is established and the government purchases any excess output and (2 ) the government buys all the farmers' output at the floor price and resells at whatever price it can get. Which scheme will taxpayers prefer? f. Consider again the two schemes. Which scheme will the farmers prefer? g. Consider again the two schemes. Which scheme will wheat buyers prefer?
Assume that the price for lawn care has fallen and sales of lawn care services have also fallen. One can conclude that
A) lawn care services are deliberately charging low prices because they want to discourage people from maintaining their own lawns. B) the demand for lawn care service has decreased. C) the law of supply has been violated. D) the number of lawn care service companies has increased.
If a firm has total revenue of $200 million, explicit costs of $190 million, and implicit costs of $30 million, its economic profit is:
a. $200 million. b. $70 million. c. $10 million. d. ?$10 million. e. ?$20 million.
Exhibit 20-3 Money market demand and supply curves
?
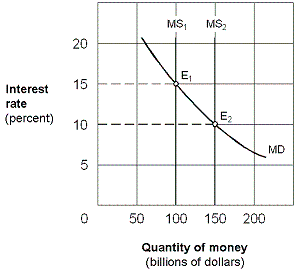
A. higher investment, lower real GDP, and lower price level. B. lower investment, lower real GDP, and lower price level. C. higher investment, higher real GDP, and higher price level. D. higher interest rate and no effect on real GDP or the price level.