Potential energy belongs to a system, and not to a single object alone
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
TRUE
You might also like to view...
A vertical outside wall of a building receives 400 W/m^2 of direct solar radiation and transfers 50 W/m^2 heat uniformly by convection to the surrounding air at 10ºC. Determine (a) vertical distance up where turbulent flow begins and (b) the wall surface temperature at this location.
What will be an ideal response?
A spherical communications satellite 2-m in diameter is placed in orbit around the earth. The satellite generates 1000 W of internal power from a small nuclear generator. If the surface of the satellite has an emittance of 0.3 and is shaded from solar radiation by the earth, estimate the surface temperature. What is the temperature if the satellite with an absorptivity of 0.2 is in an orbit in which it is exposed to solar radiation? Assume the sun is a blackbody and irradiation striking the satellite is 1366 W/m2 and state your assumptions.
GIVEN
• Spherical satellite
• Diameter (D) = 2 m
• Heat generation = 1000 W
• Emittance (?) = 0.3
• Absorptivity of satellite (?)=0.2
• Solar irradiation(G)=1366 W/m2
FIND
• The surface temperature (Ts)
• Surface temperature of satellite
ASSUMPTIONS
• The satellite radiates to space which behaves as a blackbody enclosure at 0 K
• The system is in steady state
SKETCH
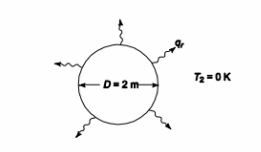
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
The Stefan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
During the nuclear epoch, the temperatures were:
A) higher than 1032 K. B) about a trillion degrees. C) comparable to the temperatures inside giant stars today. D) less than 10 million K. E) between 3,000 and 16,000 K.
At a point in space where the magnetic field is measured, the magnetic field produced by a current element
A. points radially away in the direction from the current element to the point in space. B. points radially in the direction from the point in space towards the current element. C. points in a direction parallel to the current element. D. points in a direction parallel to but opposite in direction to the current element. E. points in a direction that is perpendicular to the current element and perpendicular to the radial direction.