Summarize the steps involved with the inflammatory response. What will be an ideal response?
ANSWER: In the area around a wound, white blood cells called macrophages detect and bind to
molecules on the surface of the invading bacteria. Binding to the bacterial cell activates the
macrophage, which then engulfs and destroys the bacteria. Activated macrophages also
secrete chemical signal molecules called cytokines. The cytokines, along with histamine
secreted by activated mast cells in the area of infection, cause nearby capillaries to dilate,
increasing blood flow to the area (this is why the area around a cut or scrape gets red and
warm). The heat creates an unfavorable environment for bacterial growth, mobilizes
additional white blood cells, and raises the metabolic rate in nearby cells. These reactions
promote healing. The cytokines also make the blood vessel all sticky, causing neutrophils to
attach. Chemokines attract neutophils, which pass between cells of the blood vessel wall and
migrate to the infection site and flood into the area, engulfing and destroying the invading
bacteria.
If infection persists, clotting factors in blood plasma trigger a cascade of small blood clots
that seal off the injured area, preventing the escape of invading organisms, recruiting more
white blood cells to destroy the invading bacteria. Finally, the area is targeted by white blood
cells that clean up dead bacteria and dispose of dead cells and debris.
You might also like to view...
When preparing a smear from a viscous and granular sample the microbiologist should:
a. add saline to the sample to thin out the specimen for smear preparation. b. place some of the material in an enrich-ment broth and then use the broth for smear preparation. c. use a sterile swab and roll it around in the material because it will be easier to roll the sample than to use a loop on the slide. d. if the material is not able to be distributed using a sterile loop or swab, use a squash or crush prep to spread out sample.
Which answer best describes energy flow in biological systems as described in the text?
a. glucose ? G3P ? NADH ? ATP b. bacteria ? archaea ? plants ? animals c. NAD+ ? NADH ? ADP ? ATP d. G3P ? glucose ? ATP ? NAD+ e. pyruvate oxidation ? glycolysis ? fermentation ? citric acid cycle
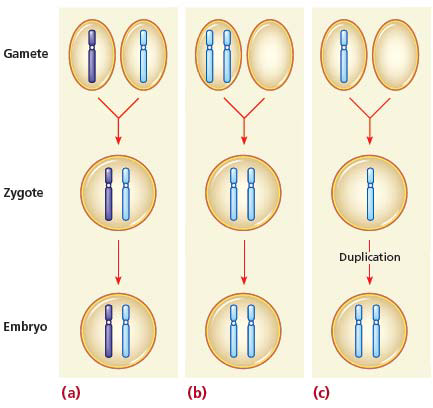
Describe normal embryo formation and two mechanisms of nondisjunction represented in the figure and identify the consequences of these chromosomal anomalies
A variant of the icosahedral shape found in some bacteriophages is called:
a. Complex b. Helical c. Prolate d. Nucleic e. Enveloped