Policies that reduce the incentive for households to save include
a. means-testing.
b. College and university financial aid administration.
c. inheritance taxes.
d. All of the above.
d
You might also like to view...
If we are currently at point T, we can get to point S in the long run
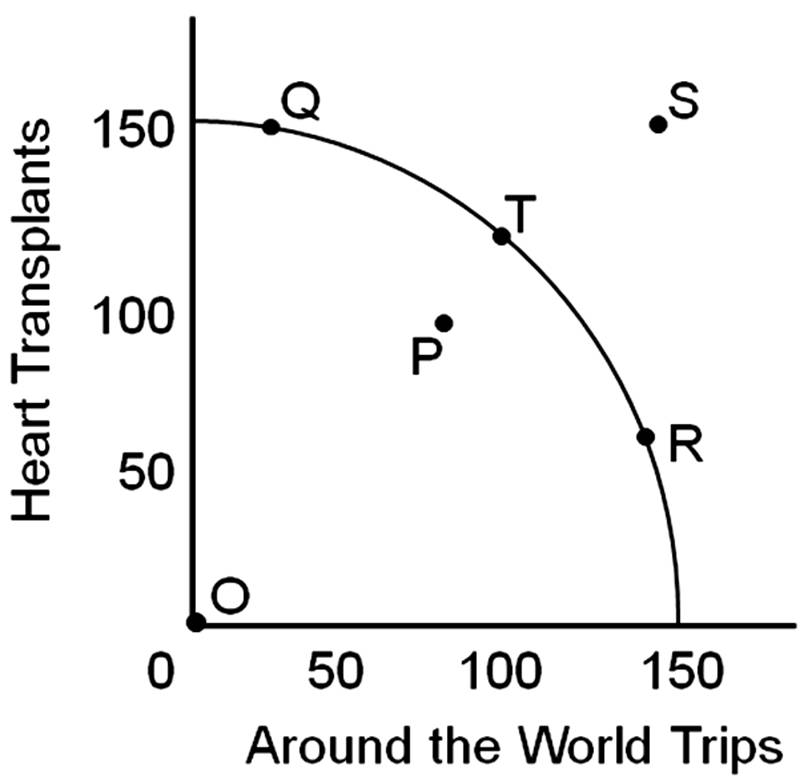
A. through economic growth over a period of years.
B. immediately by using resources more efficiently.
C. immediately by reducing the unemployment rate.
D. immediately through technological development.
Other things the same, bonds are likely to have higher interest rates if they have
a. tax exemptions and short terms. b. tax exemptions and long terms. c. no tax exemptions and short terms. d. no tax exemptions and long terms.
Suppose Jordan and Lee are trying to decide what to do on a Friday. Jordan would prefer to see a comedy while Lee would prefer to see a documentary. One documentary and one comedy are showing at the local cinema. The payoffs they receive from seeing the films either together or separately are shown in the payoff matrix below. Both Jordan and Lee know the information contained in the payoff matrix. They purchase their tickets simultaneously, ignorant of the other's choice.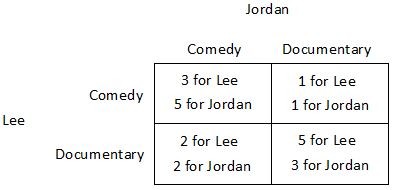 Suppose a timing element is added to the game, and that Jordan buys a ticket first. Then, after seeing Jordon's choice, Lee buys a ticket. What will be the equilibrium outcome?
Suppose a timing element is added to the game, and that Jordan buys a ticket first. Then, after seeing Jordon's choice, Lee buys a ticket. What will be the equilibrium outcome?
A. Jordan will buy a ticket to the documentary and Lee will buy a ticket to the comedy. B. Jordan will buy a ticket to the comedy and Lee will buy a ticket to the documentary. C. Both Jordan and Lee will buy a ticket to the documentary D. Both Jordan and Lee will buy a ticket to the comedy.
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 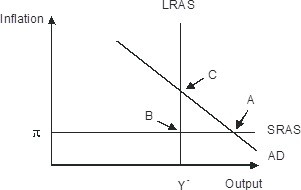
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward