Solve the equation in part (a) graphically, expressing the solution to the nearest hundredth. Then, use the graph to solve the associated inequalities in parts (b) and (c), expressing endpoints to the nearest hundredth.(a)  = 0; (b)
= 0; (b)  > 0; (c)
> 0; (c)  < 0
< 0
A. (a) {-2.77} (b) (2.92, ?) (c) (-?, 2.92)
B. (a) {8.5} (b) (8.5, ?) ? (-?, -1.14) (c) (-1.14, 2.92)
C. (a) {2.92} (b) (2.92, ?) ? (-?, -1.14) (c) (-1.14, 2.92)
D. (a) {-1.14} (b) (-1.14, ?) (c) (-?, -1.14)
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Give the first five terms of the sequence for which an is given.an = 3n - 1, n = 1, 2, 3...
A. -2, -5, -8, -11, -14 B. 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 C. 2, 5, 8, 11, 14 D. 4, 7, 10, 13, 16
Use the figure below to answer the following question(s).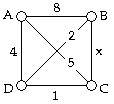 The cheapest-link tour starting with vertex A is uniquely A, B, D, C, A
The cheapest-link tour starting with vertex A is uniquely A, B, D, C, A
A. only if 1 < x < 2. B. only if x > 2. C. only if x > 5. D. only if 0 < x < 1. E. regardless of the value of x.
Consider the following squares. For the nth square, the length of each side is n. i)Find the areas of the first 4 squares, then list the areas in a sequence.ii) Find the general term for the area of the nth square in the sequence. Use an for the area.
i)Find the areas of the first 4 squares, then list the areas in a sequence.ii) Find the general term for the area of the nth square in the sequence. Use an for the area.
What will be an ideal response?
Divide.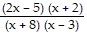 ÷
÷ 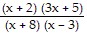
A. 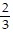
B. 
C. 
D. - 