The Laffer curve depicts a basic idea of which of the following schools?
a. supply-side economics
b. rational expectations
c. Keynesian
d. neo-Keynesian
e. classical
A
You might also like to view...
Which of the following describe the United States' unemployment rate over the last 80 years?
i. The unemployment rate has decreased each year since the Great Depression. ii. The unemployment rate has averaged about 5.7 percent since 1929. iii. Job creation due to defense spending and consumer spending in the 1960s drove the unemployment rate to one of its lowest level. A) i and ii only B) ii and iii only C) i, ii and iii D) i only E) i and iii
Slick Shades has a constant marginal cost of production equal to $80 and the distributors have a constant marginal cost of distribution equal to $30. If Slick Shades vertically integrates with the perfectly competitive distributors, the relevant demand curve for the combined firm is the ________ demand curve and the combined firm's marginal cost is equal to ________.
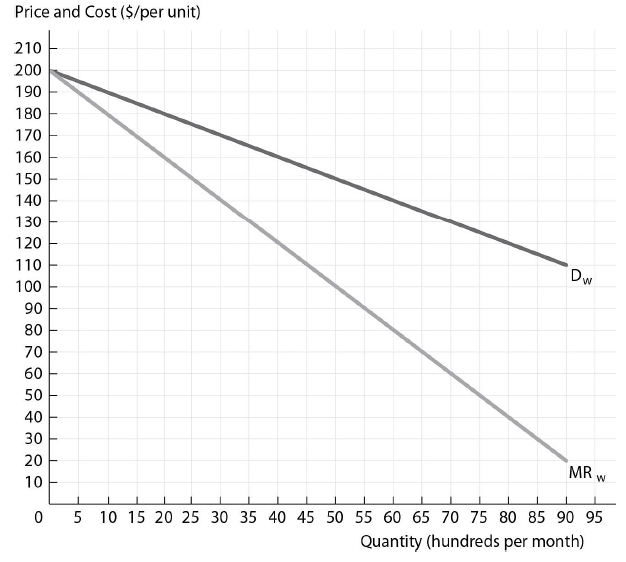
The figure above shows the wholesale demand and marginal revenue curves for Slick Shades Sunglasses, a sunglasses firm with market power. Slick Shades Sunglasses has a constant marginal cost of production and it sells to perfectly competitive independent retail distributors that have a constant marginal cost of distribution.
A) retail; $110
B) retail; $80
C) wholesale; $110
D) wholesale; $80
Assume a simplified banking system in which all banks are subject to a uniform reserve requirement of 20 percent and checkable deposits are the only from of money. A bank that received a new checkable deposit of $10,000 would be able to extend new loans up to a maximum of:
a. $2,000 b. $8,000. c. $9,000 d. $10,000.
Suppose there are two types of people: "good risks" who have 1 to 9 odds of falling ill, and "bad risks" who have a 1 to 3 odds of falling ill. If an insurance company cannot distinguish good risks from bad risks, what is the best way for it to deal with this problem?
a. Do not offer any insurance at 1 to 3 odds. b. Make everyone purchase insurance that offers 1 to 3 odds. c. Limit the amount of insurance that can be purchased at 1 to 9 odds. d. Provide policies that offer 1 to 9 odds and 1 to 3 odds, allowing each group to purchase the appropriate policy.