The price elasticity of demand for kale in Texas is -2, and the price elasticity of demand for kale in California is -0.5. In other words, demand in Texas is ________, and demand in California is ________.
A. inelastic; unit inelastic
B. inelastic; elastic
C. elastic; unit elastic
D. elastic; inelastic
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Oligopolies can arise as a result of both natural barriers and government created barriers
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Prices in both the U.S. and China rise, but prices in China increase by a larger percentage. According to purchasing-power parity, the U.S. dollar
a. gains value both in terms of the domestic goods and services it can buy and in terms of the Chinese currency it can buy. b. gains value in terms of the domestic goods and services it can buy, but loses value in terms of the Chinese currency it can buy. c. loses value in terms of the domestic goods and services it can buy, but gains value in terms of the Chinese currency it can buy. d. loses value both in terms of the domestic goods and services it can buy and in terms of the Chinese currency it can buy.
If Ana devotes all her time to making fudge, she can make 3 pounds of fudge an hour, and if she devotes all her time to making toffee, she can make 2 pounds of toffee an hour. If Leo devotes all his time to making fudge, he can make 4 pounds of fudge an hour, and if he devotes all his time to making toffee, he can make 5 pounds of toffee an hour. Suppose that Ana and Leo decide to work together as a team. Can they produce 2 pounds of fudge and 4.5 pounds of toffee each hour?
A. No, this point is not attainable. B. Yes, this point is both attainable and efficient. C. No, this point is not attainable and inefficient. D. Yes, this point is attainable, but inefficient.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.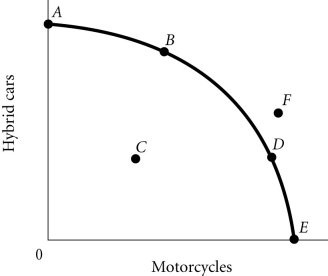 Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, as the economy moves from Point D to Point B, the opportunity cost of hybrid cars, measured in terms of motorcycles,
Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, as the economy moves from Point D to Point B, the opportunity cost of hybrid cars, measured in terms of motorcycles,
A. initially increases, then decreases. B. increases. C. remains constant. D. decreases.