When growth goes down, unemployment tends to go:
A. down at the same time, and vice versa.
B. up at the same time, but remains sticky on the way down and lags behind.
C. down shortly after, and vice versa.
D. up shortly after, and vice versa.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is a weakness in trying to get the wealthy to bear more of the burden of increasing growth in a less developed country?
a. The wealthy do not have significant political power. b. The wealthy can move their savings to other countries. c. The wealthy do not have much money to tax. d. The wealthy have large homes in their country and so are less likely to leave. e. The wealthy have powerful businesses that they are unable to relocate.
Based on the graphs showing price discrimination in movie ticket prices, an elastic demand curve prompts theatres to ______.
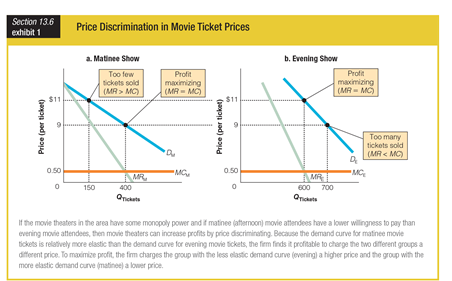
a. charge higher prices
b. charge lower prices
c. go bankrupt
d. add more seats
Under the rational expectations hypothesis, which of the following is the most likely short-run effect of a move to expansionary monetary policy?
A. a higher general level of prices but no change in real output B. a higher general level of prices and an expansion in real output C. no change in the general level of prices and a reduction in real output D. no change in either the general level of prices or real output
The monopsonistic exploitation of labor refers to
A. the union wage differential. B. the reduction in total output from monopoly in the product market. C. workers being paid a wage less than their marginal revenue product. D. the reduction in employment resulting from union wage setting.