What do halo stars do differently from disk stars?
A) Halo stars orbit the galactic center with many different inclinations, while disk stars all orbit in nearly the same plane.
B) Halo stars remain stationary, quite unlike disk stars that orbit the galactic center.
C) Halo stars explode as supernovae much more frequently than disk stars.
D) Halo stars orbit the center of the galaxy at much lower speeds than disk stars.
A) Halo stars orbit the galactic center with many different inclinations, while disk stars all orbit in nearly the same plane.
You might also like to view...
Compare the planar atom density of the {100}-type planes with the {111}-type planes in the FCC structure of copper that has a lattice parameter of 0.361 nm.
What will be an ideal response?
Modern evidence based on what can be determined about the products of nuclear reactions in the first few minutes after the big bang shows that dark matter:
A) does not have any density. B) does not exist. C) is not present in galaxies. D) is not baryonic.
An air-cooled low-pressure-steam condenser is shown in following figure.
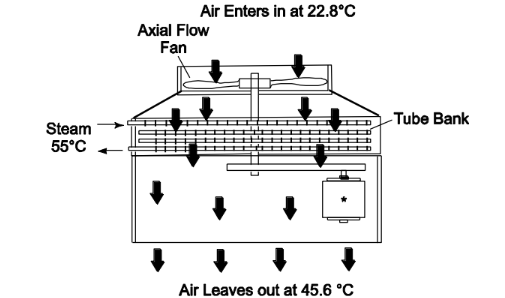
An air-cooled low-pressure-steam condenser is shown in following figure.
The tube bank is four rows deep in the direction of air flow and there are total of 80 tubes. The tubes have ID = 2.2 cm and OD 2.5 cm and are 9-m-long with circular fins on the outside. The tube-plus-fin area is 16 times the bare tube area (i.e., the fin area is 15 times the bare tube area, neglect the tube surface covered by fins). The fin efficiency is 0.75. Air flows past the outside of the tubes. On a particular day, the air enters at 22.8°C and leaves at 45.6°C. The air flow rate is 3.4 × 105 kg/h. The steam temperature is 55°C and has a condensing coefficient of 104 W/(m2 K). The steam-side fouling coefficient is 104 W/(m2K). The tube wall conductance per unit area is 105 W/(m2K). The air-side fouling resistance is negligible. The air-side-film heat transfer coefficient is 285 W/(m2K). (Note this value has been corrected for the number of transverse tube rows.) (a) What is the log-mean temperature difference between the two streams? (b) What is the rate of heat transfer? (c) What is the rate of steam condensation? (d) Estimate the rate of steam condensation if there were no fins.
GIVEN
• The condenser shown above
• Number of tubes (N) = 80 and number of rows (Nr) = 4 (in air flow direction)
• Tube diameters Di = 2.2 cm = 0.022 m Do = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
• Tube length (L) = 9 m
• Air temperature Ta,in = 22.8°C Ta,out = 45.6°C
• Air flow rate m a= 3.4 × 105 kg/h = 94.4 kg/s
• Steam temperature = 55°C (constant)
• Fin area = 15 (tube area)
• Fin efficiency (?f) = 0.75
• Steam side
Transfer coefficient h i= 104 W/(m2 K)
Fouling coefficient (1/Ri) = 104 W/(m2 K)
• Tube wall conductance per unit area (1/Rk) = 105 W/(m2 K)
• Air side: Transfer coefficient h o= 285 W/(m2 K)
• Fouling resistance on the air side is negligible
FIND
(a) The log-mean temperature difference(LMTD)
(b) The rate of heat transfer (q)
(c) The rate of steam condensation m
(d) Estimate the rate of steam condensation if there were no fins 2cm
ASSUMPTIONS
• Air side transfer coefficient is the same with or without fins
• Tube surface covered by the fins is negligible
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the average temperature of 34.2°C,
the specific heat (cpa) = 1013 J/(kg K),
for steam at a saturation temperature of 55°C,
the heat of vaporization (hfg) = 2600 (kJ/kg)
Breadcrumb trails are best suited to large websites with a hierarchical structure.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)