After one year, a company will pay $20 in dividends. It commits to paying $21 two years from the current date. This growth rate in dividends is expected to continue indefinitely. The interest rate is 8%. Compute the current price of this stock, using the dividend-discount model.
What will be an ideal response?
First, we need to compute the growth rate of dividends, g. This is equal to 5% = ($21 - $20)/$20.
Now, we can compute the price of the stock:
Ptoday = Dtoday(1 + g)/(i - g)
Ptoday = $20(1 + 0.05)/(0.08 - 0.05)
Ptoday = $700
You might also like to view...
Refer to the scenario above. Which of the following will happen in equilibrium if the game is played only once?
A) Social surplus will be maximized. B) Tom will trust Harry and Harry will defect. C) Tom will trust Harry and Harry will cooperate. D) Neither of them will make any money.
A higher nominal money supply is equally demanded, given each level of income, at a ________ interest rate, meaning that the LM curve has shifted to the ________
A) higher, left B) higher, right C) lower, left D) lower, right
Suppose the production function for coffee (C) is C = min(B,W), where B = beans in pounds and W = water in gallons. Suppose the price of water is $.10 per gallon and the price of beans is $10 per pound. The expansion path
a. depends on the price of beans only. b. depends on the price of water only c. depends on the price of neither beans nor water. d. depends of the costs of both beans and water.
In Figure 32.1, at the market price-quantity combination, the consumer surplus is 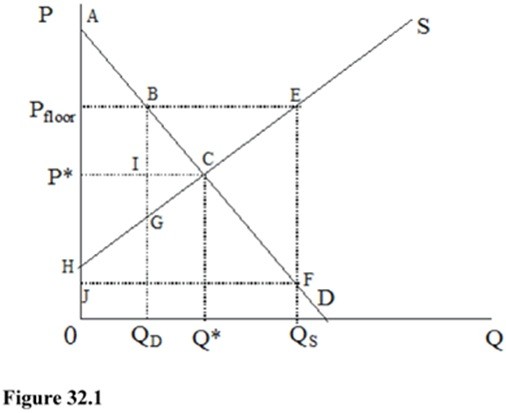
A. HPfloorBG. B. APfloorB. C. P*AC. D. HP*C.