When using the terms "total utility" or "marginal utility" we assume:
a. the consumer will exchange one commodity for another
b. the consumer will part with money for the commodity
c. the consumer has declined to purchase the commodity
d. a and b are correct
b
You might also like to view...
Where marginal cost is less than average total cost,
a. opportunity cost must have been excluded from the calculation of marginal cost. b. marginal cost must be falling. c. marginal cost must be rising. d. marginal cost may be rising, falling, or constant.
The diagram below shows the production possibilities frontier (PPF) for a country that produces guns (G) and butter (B). Most people in the country prefer guns, so in the absence of international trade, point A represents the combination of G and B that maximizes welfare. The slope of the PPF at point A is equal to -2. 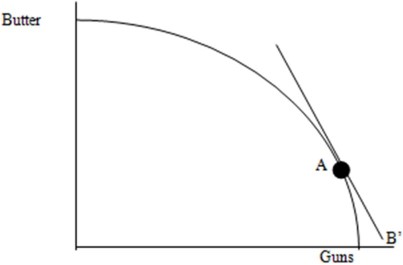 Over the long run, do you think this country would be better off by shifting its production towards guns or butter? Please identify the most efficient production point in the PPF with trade. What would be the ratio of the prices at that point?
Over the long run, do you think this country would be better off by shifting its production towards guns or butter? Please identify the most efficient production point in the PPF with trade. What would be the ratio of the prices at that point?
What will be an ideal response?
The "fiscal multiplier" is the ripple effect of subsequent:
A. increases in spending following an initial increase in government spending. B. increase rate changes following a change to the federal funds rate. C. increases in lending following an initial increase in bank reserves. D. private-sector layoffs following an initial layoff in the public sector.
Thinking up a new idea is an example of
A. social overhead capital. B. human capital accumulation. C. an innovation. D. an invention.