Having a competitive advantage emanates from
a. Increased price
b. Decreased cost
c. One or both of the above
d. None of the above
c
You might also like to view...
The following table shows the relationship between the speed of a computer's CPU and its benefits and costs. Assume that all other features of the computer are the same (that is, CPU speed is the only source of variation), and only the CPU speeds listed below are available for purchase.CPUGHzTotal BenefitMarginal BenefitTotal CostsMarginal Costs2.0$1,000 $900 2.5$1,400 &1003.0 $300$1,200 3.5$1,900 &1,500 4.0$2,000 &400The total benefit of a 3.0GHz computer is:
A. $900. B. $300. C. $1,700. D. $1,650.
Unless you accept his 'final offer' your opponent threatens to scrap the whole deal:
a. His threat is more believable if both parties would be harmed by scrapping the deal b. His threat is more believable if he has better outside options c. His threat is more believable if only he is hurt from the deal falling through d. His threat is more believable if he has balked at this course of action in the past
If bond prices rise,
A) interest rates rise, which in turn, discourage investment. B) interest rates fall, which in turn, discourage investment. C) interest rates rise, which in turn, stimulate investment. D) interest rates fall, which in turn, stimulate investment.
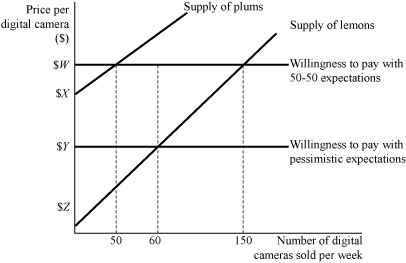
 Figure 9.4 represents the market for used 12 megapixel digital cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $400 for a plum (high-quality) used digital camera and $200 for a lemon (low-quality) used digital camera. If buyers believe that 50% of used digital cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), what is consumers' willingness to pay ($W)?
Figure 9.4 represents the market for used 12 megapixel digital cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $400 for a plum (high-quality) used digital camera and $200 for a lemon (low-quality) used digital camera. If buyers believe that 50% of used digital cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), what is consumers' willingness to pay ($W)?
A. $100 B. $200 C. $300 D. $400