A gas in a furnace has an extinction coefficient of 0.01m^-1 and a mean beam length of 10 m. What is the transmissivity of radiation through the gas?
What will be an ideal response?
The transmissivity is related to the extinction coefficient by
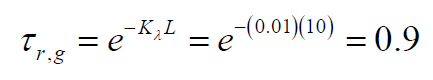
You might also like to view...
Hot flue gases from a combustion furnace flow through a chimney, which is 7-m-tall and has a hollow cylindrical cross section with inner diameter di = 30 cm and outer diameter do = 50 cm. The flue gases flow with an average temperature of Tg = 300°C and convective heat transfer coefficient of hg = 75 W/(m2 K). The chimney is made of concrete, which has a thermal conductivity of k = 1.4 W/(m K). It is exposed to outside air that has an average temperature of Ta = 25°C and convective heat transfer coefficient of 15 W/(m2 K). For steady-state conditions, (a) determine the inner and outer wall temperatures, (b) plot the temperature distribution along the thickness of the chimney wall, and (c) determine the rate of heat loss to outside air from the chimney. Solve the problem by numerical
analysis using a nodal network with ?r = 2 cm and ?? = 10°.
GIVEN
- Hot flue gas flow in a hollow cylindrical 7-m-tall chimney with inner and outer diameters of
di = 0.3 m and do = 0.5 m, and thermal conductivity k = 1.4 W/(m K).
- Average hot gas temperature Tg = 300°C and heat transfer coefficient
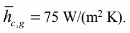
- Outside air average temperature Ta = 25?C and heat transfer coefficient
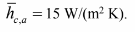
FIND
- The temperature distribution in chimney wall and the inside and outside wall temperatures.
- Rate of heat loss from gas to outside air through the chimney.
ASSUMPTIONS
- Steady state conditions, and there is no heat generation in the chimney wall and the conduction
along the height of the chimney is negligible.
In the wave model, light is ________.
A. a mix of electric and magnetic energy B. a packet of energy moving through space C. a compression wave moving through the air D. a ripple in space-time E. the absence of dark
You observe the peak brightnesses of two white dwarf supernovae. Supernova A is only 1/4 as bright as Supernova B. What can you say about their relative distances?
A) Supernova A is twice as far away as Supernova B. B) Supernova A is 4 times as far away as Supernova B. C) Supernova B is 4 times as far away as Supernova A. D) Supernova B is twice as far away as Supernova A. E) We can't say anything about their relative distances because we do not have enough information.
The closest terrestrial analog to hours of right ascension is angle of longitude
Indicate whether the statement is true or false