The objective of bank management is to
A. maximize stockholders’ profits by making risky investments and giving loans to borrowers who will pay the highest interest rates.
B. refuse to make risky loans and make loans only to the safest borrowers.
C. invest in the U.S. government securities and make loans only to established businesses.
D. strike the appropriate balance between the attraction of bank profits and the need for bank safety.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
If saving supply decreases, the equilibrium real interest rate ________ and the equilibrium quantity of investment ________
A) rises; decreases B) falls; decreases C) falls; increases D) rises; increases E) does not change; does not change
A production possibilities frontier shows
A) the various combinations of output a nation can produce a certain time, given its available resources and technology. B) the limits to future growth of a nation. C) how money can be allocated among two kinds of goods. D) that if price of one good decreases, the price of the other has to increase. E) that it is impossible to produce inefficiently.
A consumer has preferences over two goods, X and Y. Suppose we graph this consumer's preferences (which satisfy the usual properties of indifference curves) and budget constraint on a diagram with X on the horizontal axis and Y on the vertical axis. At the consumer's current consumption bundle, the consumer is spending all available income, and the marginal rate of substitution is greater than
the slope of the budget constraint. We can conclude that the consumer a. is currently maximizing satisfaction subject to the budget constraint. b. could increase satisfaction by consuming more X and less Y. c. could increase satisfaction by consuming less X and more Y. d. could purchase more X and more Y and increase total satisfaction.
The figure below shows the market for computers in a small importing country. Dd and Sd are the domestic demand and supply curves of computers, respectively.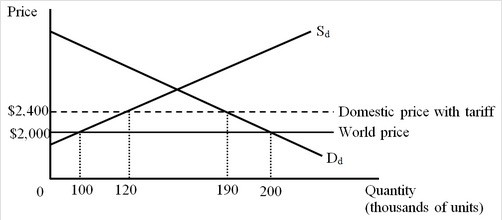 The consumption effect of the tariff on computers is worth
The consumption effect of the tariff on computers is worth
A. $76 million. B. $78 million. C. $2 million. D. $4 million.