Explain the endowment effect
What will be an ideal response?
The endowment effect refers to the tendency of people to be unwilling to sell a good they already own even if they are offered a price that is greater than the price they would be willing to pay to buy the good if they did not already own it. This inconsistency comes from a failure to take into account nonmonetary opportunity costs.
You might also like to view...
Explain why a monopoly or a perfectly competitive firm does not consider a rival firm's behavior, but an oligopoly and a monopolistically competitive firm do
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following best illustrates the fallacy of composition?
a. If I stand up at a baseball game I will be able to see the game better; if all fans stood up at a baseball game they would all be able to see the game better. b. If I wore a jacket to a baseball game in October, I would be warmer; if all fans wore jackets they would all be warmer. c. If I purchase fewer concessions at a baseball game, I will save money; if all fans purchase fewer concessions then all can save money. d. If I yell more during a baseball game it will be louder if all fans yell more during the game it will be much louder.
Under current federal antipoverty programs,
A. economic equality is promoted at the least possible cost in economic efficiency. B. a family’s benefits do not depend on its earnings from work. C. a family’s total income (cash and in-kind benefits) may actually fall if its earnings from work rise. D. families with children are entitled to no more assistance than families without children.
This graph shows three different budget constraints: A, B, and C.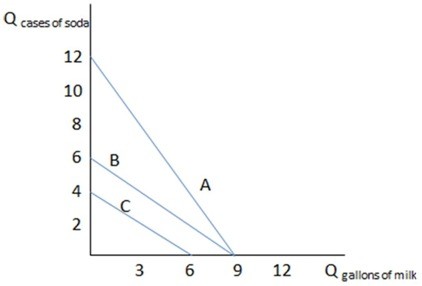 If Bart has budget constraint A in the graph shown, what would cause his budget constraint to shift to B?
If Bart has budget constraint A in the graph shown, what would cause his budget constraint to shift to B?
A. The price of soda has decreased. B. The price of milk has increased. C. Bart's income has decreased. D. The price of soda has increased.