A 300-g glass thermometer initially at 25°C is put into 200 cm3 of hot water at 95°C. Find the final temperature (in °C) of the thermometer, assuming no heat flows to the surroundings. (The specific heat of glass is 0.2 cal/g/°C.)
a. 52
b. 68
c. 89
d. 79
e. 36
d
You might also like to view...
At what, if any, temperature are the numerical readings on the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales the same?
A) -30° B) -40° C) -50° D) -60° E) They can never read the same because they are based on different zeroes.
From a stationary position, I observe a moving boxcar, which has a mirror along the front wall, but it is open at the back of the boxcar. I send a flash of light from my flashlight and time the flash of light as it goes to the front of the boxcar and returns to the back of the boxcar. A passenger in the boxcar also times the round trip of the flash of light. Compare the times recorded on our
watches. a. The time recorded on the two watches is the same. b. The time recorded on his watch is shorter. c. The time recorded on his watch is longer. d. The answer depends on the reference system you are in.
A 10 kg solid cylinder (I = 1/2 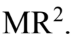 ) with a radius of 30.0 cm is rotating about a vertical axis through its center. If the angular momentum is increasing at the rate of 25 kg
) with a radius of 30.0 cm is rotating about a vertical axis through its center. If the angular momentum is increasing at the rate of 25 kg 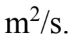 then what is the torque?
then what is the torque?
A. 70 N•m B. 45 N•m C. 37 N•m D. 25 N•m E. 12 N•m
Superconductors have been discussed as a means for electrical energy storage. Because they are resistanceless, a current once started in a loop would continue without loss. If a current of 1.0 × 10^4 A were started in a huge toroidal coil of radius 1.0 km and inductance 50 H, how much electrical energy (in kWh) could be stored?
a. 300 kWh b. 480 kWh c. 690 kWh d. 840 kWh