Which of the following is true?
a. Total utility is the aggregate level of satisfaction that results from consumption of a given number of goods and services.
b. Marginal utility is the additional satisfaction generated by the last unit of a good that is consumed
c. Total utility equals marginal utility of the last unit times the number of units consumed.
d. Both a. and b. are true.
d
You might also like to view...
In 2008, the Treasury and Federal Reserve took action to save large financial firms such as Bear Stearns and AIG from failing. Which of the following is one reason why these measures were taken?
A) The bankruptcy of a large financial firm would force the firm to sell its holdings of securities, which could cause other firms that hold these securities to also fail. B) The Emergency Economic Stabilization Act required the Fed and the Treasury to provide financial assistance to firms that participated in regular open market actions with the Fed. C) The failure of these firms would have forced the Fed to increase interest rates, which could have led to a severe recession. D) The Fed and the Treasury wanted to allow Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae more time to buy the firms before they went bankrupt.
The original mission of the World Bank was to
A) provide capital to underdeveloped countries. B) provide capital to firms around the world. C) provide financial assistance for the reconstruction of war-damaged nations. D) provide a safe place for people around the world to put their money. E) help countries manage their exchange rates.
If the Fed sells a T-bill to a commercial bank, how will this affect the money supply?
a. It will increase the money supply. b. It will increase bank reserves. c. It will decrease the money supply. d. It will have no effect on the money supply.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.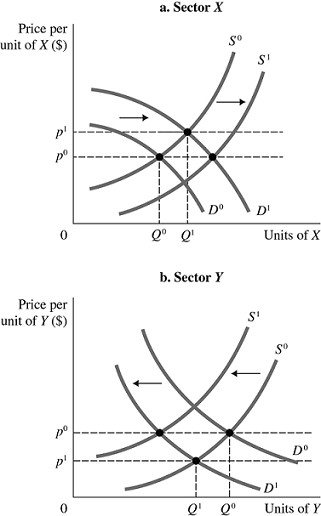 Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, a new general equilibrium will eventually be reached in sector Y with a price of ________ and a quantity of ________.
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, a new general equilibrium will eventually be reached in sector Y with a price of ________ and a quantity of ________.
A. P1; Q0 B. P1; Q1 C. P0; Q0 D. P0; < Q1