A total of $50,000 was allocated to a project to detect and reduce insider theft in the ZipCar auto parts store. Two alternatives identified as Y and Z are under consideration. The overall ROR on the $50,000 is expected to be 40%, with the rate of return on the $20,000 increment between Y and Z at 15% per year. If Z is the higher first-cost alternative, (a) what is the size of the investment required in Y, and (b) what is the rate of return on Y?
What will be an ideal response?
(a) Size of investment in Y = 50,000 – 20,000 = $30,000
(b) 30,000(i*) + 20,000(0.15) = 50,000(0.40)
i* = 0.567 (56.7%)
You might also like to view...
Match the following weeds to their category
a. bull thistle c. crabgrass b. dandelion d. henbit 12. summer annual 13. perennial 14. winter annual 15. biennial
A casualty of the computer revolution is the ____. Although it is still available from some service literature providers, it has largely been replaced by computers and is now relatively uncommon.
A. owner's manual B. microfiche C. VIN D. control label
What is the maximum pressure a power steering pump provides during low speed cornering?
A) 90 psi B) 500 psi C) 250 psi D) 1400 psi
In a semiconductor material, the net charge is zero. This requires the density of positive charges to be equal to the density of negative charges. Both charge carriers (free electrons and holes) and ionized dopant atoms have a charge equal to the magnitude of one electronic charge. Therefore the charge neutrality equation (CNE) is:
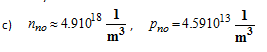
where
no = equilibrium negative carrier density
po = equilibrium positive carrier density
= ionized acceptor density
= ionized donor density
The carrier product equation (CPE) states that as a semiconductor is doped, the product of the charge carrier densities remains constant:

The semiconductor material is n- or p-type depending on whether donor or acceptor doping is greater. Almost all dopant atoms are ionized at room temperature. If intrinsic silicon is doped:
Determine:
a. If this is an n- or p-type extrinsic semiconductor.
b. Which are the majority and which are the minority charge carriers.
c. The density of majority and minority carriers.