Discuss the major environmental impacts of mining operations
What will be an ideal response?
Because mineral resources are solids which are part of the Earth's crust, extracting them can involve serious ecological disruptions, landscape alteration, and sometimes large-scale pollution of water and air. Mountaintop removal is a technique of coal extraction in which more than 100 vertical meters of a mountaintop are blasted and removed to expose deposits. This causes debris to rain down the hillsides, clogging, and polluting stream sources and thus water supplies, destroying wildlife habitats of and causing the loss of biodiversity. In the case of mining in Appalachia, physical destruction of homes buildings also occurs. Smelting of iron and other ores may produce large of amounts of sulfur oxides which cause acid precipitation and ecosystem destruction. In mining operations that require extraction and washing techniques using water, streams, and groundwater are likely to be contaminated by sulfates (acidification) and soluble toxic metal ions such as selenium, aluminum, manganese, cadmium, and nickel. In addition, other chemicals used in the extraction process may be present in mine tailings and cause further water pollution. The operations of strip mining and open-pit mining remove extensive areas of native vegetation, damage fertile soils, and increase rates of erosion. They also can cause acid-drainage, when sulfide ores are exposed to and oxidized by atmospheric oxygen. The sulfates thus formed are mixed with rainwater and cause the same sorts of damage to soils and plants found in acid deposition from coal-fired industries and electrical generating plants.
You might also like to view...
La Paz, Bolivia
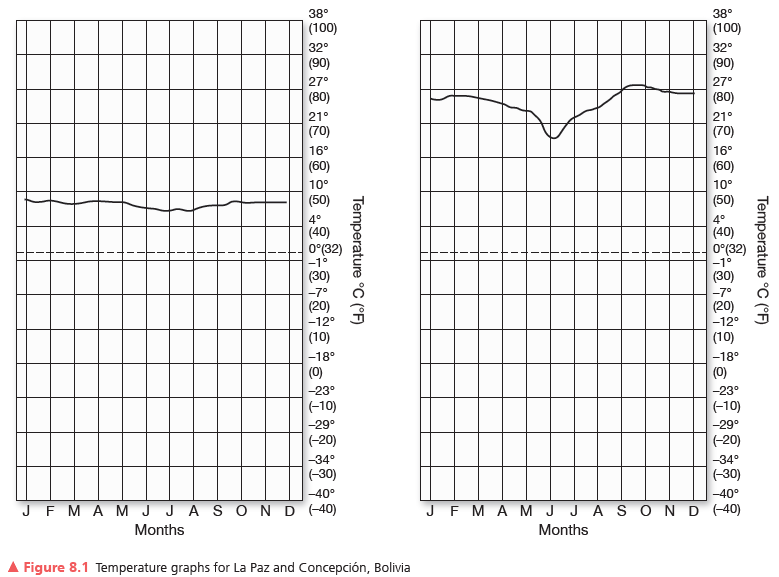
Latitude:_______ Longitude:__________
Elevation:______m_______ft
Population:________
Avg. Annual Temperature (°C, °F):________
Annual Temp. Range (°C, °F):________
What concept describes Earth’s crust as “floating” on denser underlying mantle?
a. outwash b. accretion c. isostasy d. cyclothem e. interglacial stage
Stability of earth materials on slopes depends on the balance of gravitational and frictional forces. Which of the following does NOT have a measurable effect on the balance between gravity and friction?
A. presence of water B. steepness of a slope C. atmospheric air pressure D. types of vegetation on the slope E. type of rock or sediment that is making up the slope
The albedo of the earth in a warming climate
A. decreases because of clouds that result from increased evaporation of sea water. B. increases because of rising sea level. C. is part of a negative feedback cycle, where the increased albedo due to increased snow and ice coverage increases the effectiveness of solar energy in warming land areas. D. is part of a negative feedback cycle, where the increased albedo due to clouds causes a reduction in solar energy that reaches the earth, thus resulting in cooling.