Other things being equal, an increase in the number of sellers of a good will __________________ for that good.
A. increase equilibrium price and quantity
B. increase equilibrium price and decrease equilibrium quantity
C. decrease equilibrium price and increase equilibrium quantity
D. decrease equilibrium price and quantity
E. increase demand
Answer: C. decrease equilibrium price and increase equilibrium quantity
Explanation:
An increase in the number of sellers in a market of a certain good implies the quantity demanded for that good will increase, thus the equilibrium quantity will be higher. According to the demand law, if the quantity demanded goes up, the price is likely to decrease, so, the equilibrium price will be lower
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements about a monopolist is FALSE?
A) A pure monopolist is the sole supplier of one product, good, or service. B) The monopolist faces a demand curve for the entire market for that good. C) A pure monopolist is not the same as a perfect competitor. D) The monopolist faces the industry demand curve, which is upward sloping.
A perfectly elastic demand curve implies that the firm:
A. must lower price to sell more output. B. can sell as much output as it chooses at the existing price. C. realizes an increase in total revenue that is less than product price when it sells an extra unit. D. is selling a differentiated (heterogeneous) product.
Refer to Exhibit 9.2, which shows the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopolist. The demand curve faced by the monopolist at the profit-maximizing output is _____
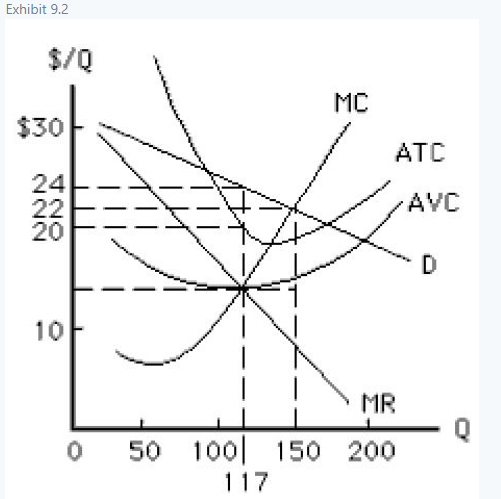
A) perfectly price elastic.
B) price elastic.
C) price inelastic.
D) unit price elastic.
E) perfectly price inelastic.
If you drive on a rural stretch of highway and come upon an intersection in which there are two gas stations, and you know them to be the only ones for 100 miles, they are
A. monopolistic competitors. B. perfect competitors. C. monopolists. D. oligopolists.