Figure 17-2
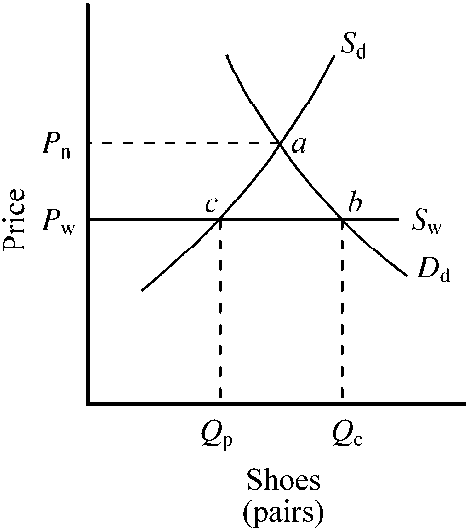
In , in the absence of trade, the domestic price of shoes is Pn. Since many foreign countries have a comparative advantage in the production of shoes, when the United States begins to trade, the domestic price will fall to the world price. When this happens, what does the quantity Qc through Qp represent?
a.
the quantity of shoes that the United States imports
b.
an increase in the world consumption of shoes
c.
the quantity of shoes that the United States exports
d.
a reduction in the world consumption of shoes
a
You might also like to view...
Teddy buys only chocolate chip cookies and hot chocolate and spends all of his income on the two items. Suppose that Teddy's marginal utility per dollar from cookies exceeds that from hot chocolate. Teddy can make himself better off if he buys
A) more cookies and less hot chocolate. B) fewer cookies and more hot chocolate. C) an equal amount of cookies and hot chocolate. D) only hot chocolate.
The aggregate demand curve slopes downward indicating that
a. an increase in the general price level will reduce the aggregate quantity of goods and services demanded. b. an increase in the general price level will increase the aggregate quantity of goods and services demanded. c. a change in the interest rate will alter the aggregate quantity of goods and services demanded. d. consumers substitute between domestic-made and foreign-made goods as their relative prices change.
Which of the following is true?
a. Specialization and trade leads to mutual gains for countries. b. Protectionism (i.e., policies that limit trade in certain goods) promotes both economic prosperity and greater employment. c. Countries that have a lot of resources, like the United States, are always hurt by trade. d. Countries will have a higher standard of living when they produce as many goods as possible domestically.
In 1929, the CPI equaled 0.171 and in 1930, the CPI equaled 0.167. These data provide evidence of a period of:
A. inflation. B. trade deficit. C. deflation. D. expansion.