In the long run,
A. all of the firm’s input quantities are variable.
B. the firm can vary the quantities of some but not all inputs.
C. managers become less efficient.
D. the total cost of producing any given level of output is greater than or equal to the short-run total cost of producing that level of output.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Starting from long-run equilibrium, a large decrease in government purchases will result in a(n) ________ gap in the short-run and ________ inflation and ________ output in the long-run.
A. expansionary; lower; potential B. expansionary; higher; potential C. recessionary; lower; potential D. recessionary; lower; lower
Recessions are periods of:
A) leftward shifts in labor supply. B) rightward shifts in labor supply. C) rightward shifts in labor demand. D) leftward shifts in labor demand.
Which of the following schools of thought reject the simple fixed-price model in favor of a model in which the aggregate supply curve is relatively flat at low levels of real GDP and slopes upward as real GDP approaches its potential level?
a. The new Keynesian b. The monetarist c. The traditional classical d. The new classical e. The Marxist
Suppose Jordan and Lee are trying to decide what to do on a Friday. Jordan would prefer to see a comedy while Lee would prefer to see a documentary. One documentary and one comedy are showing at the local cinema. The payoffs they receive from seeing the films either together or separately are shown in the payoff matrix below. Both Jordan and Lee know the information contained in the payoff matrix. They purchase their tickets simultaneously, ignorant of the other's choice.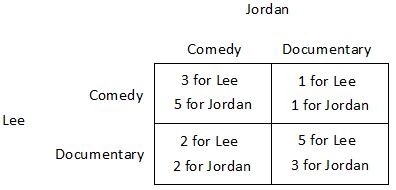 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?
A. Jordan does not have a dominant strategy. B. Jordon's dominant strategy depends on Lee's choice. C. For Jordan, seeing a documentary is a dominant strategy. D. For Jordan, seeing a comedy is a dominant strategy.