For the following question(s), consult the diagram of the human respiratory system below. Write your
answers in the spaces provided.
©2014 Brooks/Cole, Cengage Learning
Identify structure A:
Identify structure B:
Identify structure C:
Identify structure D:
Identify structure E:
Identify structure F:
Identify structure G:
Identify structure H:
Identify structure I:
Identify structure J:
Identify structure K:
Identify structure L:
ANS:A.
nasal passages
B. pharynx
C. epiglottis
D. trachea
E. lung
F. bronchi
G. bronchiole
H. alveoli
I. pleura
J. intercostal muscles
K. diaphragm
L. pulmonary capillaries
You might also like to view...
When phage ? enters the lytic cycle
A. many new copies of the phage genetic material and coat proteins are assembled to make new phages. The host cell is lysed B. many new copies of the phage genetic material and coat proteins are assembled to make new phages. The host cell remains intact. C. the genetic material of the phage is integrated into the chromosome of the bacterium. D. it immediately lyses the host cells without producing any new viruses.
Imagine a researcher is trying to genetically engineer this virus so it attacks the lung cells of a human in order to "infect" the host with a particular gene to cure a genetic disorder. Explain which structure the researcher would be most interested in working with in order to get the virus to attack the lung cell of a human.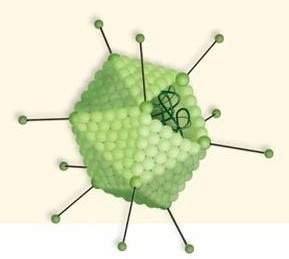
What will be an ideal response?
A triploid nucleus cannot undergo meiosis because
a. the DNA cannot replicate. b. not all of the chromosomes can form homologous pairs. c. the sister chromatids cannot separate. d. cytokinesis cannot occur. e. a cell plate cannot form.
Which chemical group is most likely to be responsible for an organic molecule behaving as a base
a. carbonyl b. amino c. hydroxyl d. carboxyl e. phosphate