The rate at which work is done is equivalent to which of the following?
a. increase in potential energy
b. thermal energy
c. potential energy
d. power
d
You might also like to view...
In the open ocean, surface currents are most affected by
A) winds, the Coriolis force, the pressure-gradient force, and land boundary conditions. B) frictional force (winds), the Coriolis force, and the pressure-gradient force. C) winds and gyres. D) both winds and the Coriolis force.
A ray of light enters a pane of glass with an angle of incidence of  The index of refraction of the glass is 1.48. What is the angle of refraction as the ray emerges from the other side of the pane?
The index of refraction of the glass is 1.48. What is the angle of refraction as the ray emerges from the other side of the pane?
A. 
B. 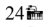
C. 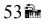
D. 
E. 
A conducting rod (length = 2.0 m) spins at a constant rate of 2.0 revolutions per second about an axis that is perpendicular to the rod and through its center. A uniform magnetic field (magnitude = 8.0 mT) is directed perpendicularly to the plane of rotation. What is the magnitude of the potential difference between the center of the rod and either of its ends?
a. 16 mV b. 50 mV c. 8.0 mV d. 0.10 mV e. 100 mV
When a solid melts,
A) the temperature of the substance increases. B) the temperature of the substance decreases. C) heat energy leaves the substance. D) heat energy enters the substance.