In a purely competitive industry, an optimal allocation of scarce resources occurs when:
A. P = AC.
B. TR = TC.
C. P = MC.
D. MR = MC.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The downside (negative aspect) associated with a free and floating exchange rates is that
a. countries appreciate their rates so that the float is only upward b. they depend on trade agreements that can, and have been, broken c. whether they increase or decrease, it takes currency to float the rate d. arbitrage takes advantage of different opportunity costs e. it creates an uncertainty about future rates that can reduce trade
If your income increases from $30,000 to $40,000 and your savings increases from $2,000 to $4,000, your marginal propensity to save (MPS) is:
A. 0.2. B. 0.4. C. 0.5. D. 0.8.
The demand curve for a monopolist is:
A. perfectly elastic. B. perfectly inelastic. C. not relevant since the monopolist sets price. D. the market demand curve.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.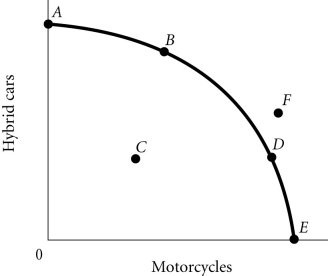 Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, Point A necessarily represents
Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, Point A necessarily represents
A. only hybrid cars being produced. B. an unattainable production point. C. what society wants. D. the economy's optimal production point.