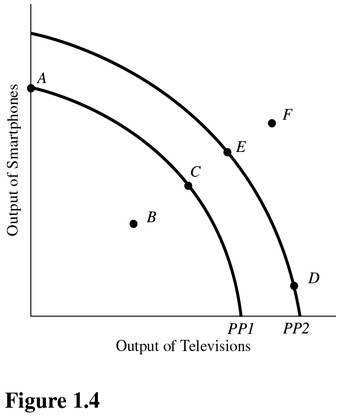
 Which of the following is true about the combination of televisions and smartphones represented by point F in Figure 1.4?
Which of the following is true about the combination of televisions and smartphones represented by point F in Figure 1.4?
A. Point F is unattainable even with advances in technology.
B. Point F is inefficient now.
C. Point F can possibly be reached if more economic resources become available or technology improves.
D. Point F will be more easily attainable if the government takes control of all privately run factories.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
If competing price searchers adjust their own prices on the basis of a close monitoring of their rival's prices,
A) all prices will tend to be the same, which proves prices are not competitive. B) all prices will tend to be the same, which proves sellers are not competing on price. C) each price searcher's demand curve will be indeterminate. D) prices will fluctuate regularly. E) prices will rise when costs increase but will not fall when costs decrease.
If an individual is maximizing his or her utility, his or her marginal rate of substitution of leisure hours for consumption will be:
a. equal to one divided by his or her wage rate. b. greater than one divided by his or her wage rate. c. equal to his or her wage rate. d. less than his or her wage rate.
Under the natural rate hypothesis, expansionary monetary and fiscal policies can at best produce a:
a. permanent change in the unemployment rate. b. short-run change in the unemployment rate. c. permanent change in the inflation rate. d. short-run change in the long-run Phillips curve.
Which of the following would tend to shift the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange in the open-economy macroeconomic model to the right?
a. the exchange rate rises b. the exchange rate falls c. the expected rate of return on U.S. assets rises d. the expected rate of return on U.S. assets falls