Refer to the graph below. Assume that the economy is initially in equilibrium at the intersection of AD1 and AS1. Suppose that there is economic growth which shifts AS1 to AS2. If the application of a monetary rule is designed to shift AD1 to AD3, but because of pessimistic business expectations AD1 only shifts to AD2, then mainstream economists would suggest that the actions to be taken to avoid deflation would be to implement a(n):
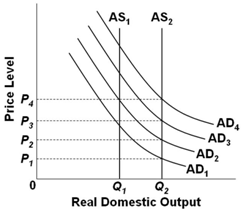
A. Expansionary fiscal policy and a tight money policy
B. Contractionary fiscal policy and a tight money policy
C. Expansionary fiscal policy and an easy money policy
D. Contractionary fiscal policy and an easy money policy
C. Expansionary fiscal policy and an easy money policy
You might also like to view...
A government policy of providing job training for unskilled youths is an example of a policy to promote economic growth by:
A. increasing the availability of natural resources. B. improving technology. C. increasing physical capital. D. increasing human capital.
Assume that Jamaica and Norway can switch between producing coolers and producing radios at a constant rate. The following table shows the number of coolers or number of radios each country can produce in one day. Output Produced in One Day Coolers Radios Jamaica 12 6 Norway 24 3 Refer to Table 3-21. Jamaica’s opportunity cost of one cooler is
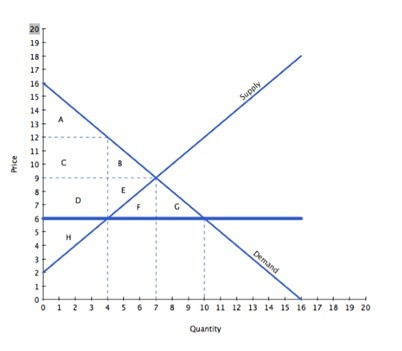 With reference to the graph above, if the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6 was a net increase in the well-being of consumers, then positive analysis would consider:
With reference to the graph above, if the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6 was a net increase in the well-being of consumers, then positive analysis would consider:
A. whether the producer surplus lost to deadweight loss is larger than the producer surplus gained from a higher price. B. whether the surplus transferred from consumers to producers is larger than the consumer surplus lost to deadweight loss. C. whether the producer surplus lost due to lower prices is larger than the producer surplus lost due to fewer transactions taking place. D. whether the surplus transferred from producers to consumers is larger than the consumer surplus lost to deadweight loss.
As the housing bubble collapsed, the cycle of defaults and falling prices began that would ultimately cause home values to:
A. stop rising, practically halting the mortgage loan industry for a number of years. B. fall by more than 90 percent in the hardest-hit areas. C. fall by more than 50 percent in the hardest-hit areas. D. fall by about 25 percent in the hardest-hit areas.