?
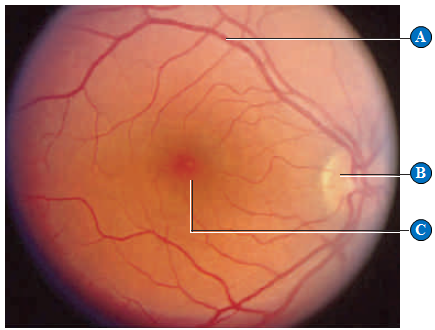
Figure 33.21C
The letter "C" in the above figure represents the ____.
A. cortex
B. cornea
C. fovea
D. blood vessels
E. optic nerve
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The Miller and Urey apparatus produced hydrogen cyanide (HCN), formaldehyde (CH2O), and glycine (an amino acid) in their first experiment, why was it important that they use water vapor, methane, carbon monoxide, ammonia and hydrogen as their reactants and an electrical spark as their energy source?
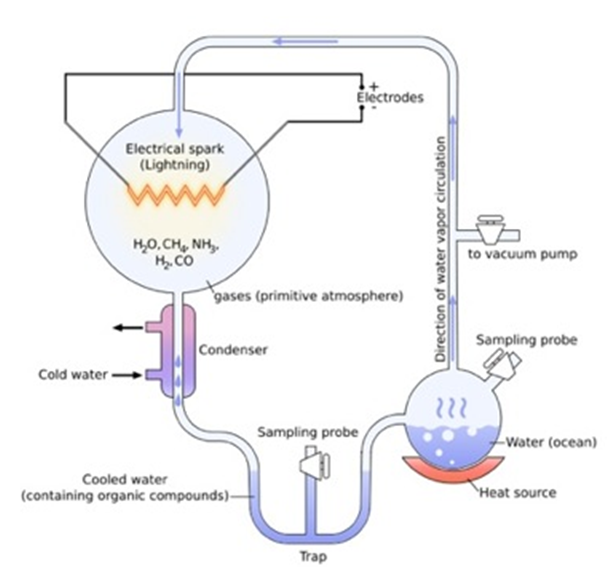
A. They knew these reactants were available in their lab and in today's atmosphere.
B. These reactants were found in today's atmosphere therefore they should be used to try to replicate the early Earth atmosphere.
C. Each of the reactants were readily changed into proteins and DNA.
D. These reactants were useful because their products were able to be predicted before the experiment began, it is always good to know the outcome of an experiment to achieve success with the experiment.
E. These reactants were hypothesized to have made up the early Earth atmosphere, the electricity was used to emulate lightening strikes.
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1. A mitochondrion has its own genome, so it can live independently from a eukaryotic cell. 2. Paternal inheritance occurs in plants but not animals because plants have chloroplasts instead of mitochondria. 3. In biparental inheritance, paternal and maternal gametes provide chloroplasts to the zygote. 4. The actions of Xist result in an organism that is a phenotypic mosaic.
The structure labeled "6" indicates
a. a primordial follicle. b. a mature follicle. c. a primordial germ cell. d. a mature germ cell. e. an ootid.
Your health care agent cannot ________
A) be any other person but your physician B) make health care decisions for you C) be younger than 12 but older that 18 years old D) be an employee of the health care provider unless he or she is a member of your family