A consumer consumes two normal goods, sandwiches and milk. When the price of milk is $0.50 per glass, the consumer purchases 40 glasses. When the price rises to $0.65 per glass, the consumer purchases 30 glasses. We can use the information provided by the consumer's optimum choices to derive the
a. demand curve for milk.
b. demand curve for sandwiches.
c. supply curve for milk.
d. labor-leisure tradeoff.
a
You might also like to view...
Player 1 and Player 2 are playing a game in which Player 1 has the first move at A in the decision tree shown below. Once Player 1 has chosen either Up or Down, Player 2, who can see what Player 1 has chosen, must choose Up or Down at B or C. Both players know the payoffs at the end of each branch. 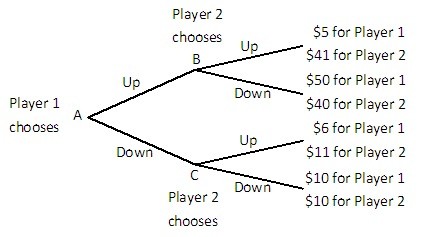 What is the equilibrium outcome of this game?
What is the equilibrium outcome of this game?
A. Player 1 chooses Up and Player 2 chooses Down. B. Player 1 chooses Down and Player 2 chooses Up. C. Player 1 and Player 2 both choose Up. D. Player 1 and Player 2 both choose Down.
Explain why you would rather be a borrower during a period of unexpected rising inflation, and a lender during a period of unexpected declining inflation
What will be an ideal response?
Taxes that are designed to discourage consumption of the taxed good are called _____
a. regressive taxes b. head taxes c. sumptuary taxes d. sales taxes
Suppose a computer manufacturer purchases a $100 case from a supplier, a $300 computer chip from another supplier, and sells the computers for $1000 . How much did the company contribute to GDP?
a. $1000 b. $900 c. $700 d. $600 e. $400