Which of the following could explain why the demand for table salt is inelastic?
A) Salt is a luxury good.
B) Salt is a rare commodity.
C) Households devote a very small portion of their income to salt purchases.
D) Salt is a luxury for high-income consumers but a necessity for low-income consumers.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
If the Fed decides to increase interest rates to fight off potential inflation, and their policy action kept the inflation rate stable, then other things equal, this would result in
A) the IS curve shifting to the right. B) the IS curve shifting to the left. C) the MP curve shifting up. D) the MP curve shifting down.
A World View article titled "Japan Sees Quake Damage Bill of Up to $309 Billion, Almost Four Katrinas" implies that the most likely impact from power shortages from this destruction would be
A. A leftward shift of aggregate supply. B. An increase in GDP. C. A rightward movement down the Phillips curve. D. A decrease in inflation.
Why do economies of scale and learning curve effects look similar when they are graphed? What different concepts do they represent?
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the information provided in Table 33.3 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Table 33.3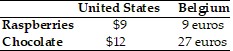 Refer to Table 33.3. If the exchange rate is $1 = 2 euros, then
Refer to Table 33.3. If the exchange rate is $1 = 2 euros, then
A. the United States will import both raspberries and chocolate. B. the United States will import raspberries and Belgium will import chocolate. C. Belgium will import both raspberries and chocolate. D. Belgium will import chocolate.