If the interest rates in an economy are close to zero, _____
a. there will be an excess demand for loanable funds
b. the economy will be likely to fall into a liquidity trap
c. expansionary monetary policy will be effective, but not contractionary monetary policy
d. contractionary monetary policy will be effective, but not expansionary monetary policy
b
You might also like to view...
Explain how a country with a current account deficit is a ripe candidate for currency devaluation
What will be an ideal response?
In a free market, the market price and quantity in the above figure will adjust to equilibrium values of
A) $1 per gallon and 50 million gallons. B) $4 per gallon and 10 million gallons. C) $2 per gallon and 60 million gallons. D) $2 per gallon and 30 million gallons.
The presence of adverse selection in a market causes:
A. some transactions to fail to take place. B. market failure. C. a deadweight loss. D. All of these statements are true.
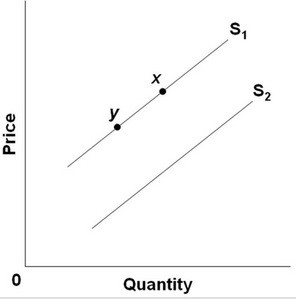 Refer to the above diagram for good R. A shift in the supply curve from S2 to S1 would best be explained by:
Refer to the above diagram for good R. A shift in the supply curve from S2 to S1 would best be explained by:
A. government imposing a tax on good R. B. an improvement in the technology used to produce good R. C. a decrease in the price of resources used to produce good R. D. an increase in the price of good R.