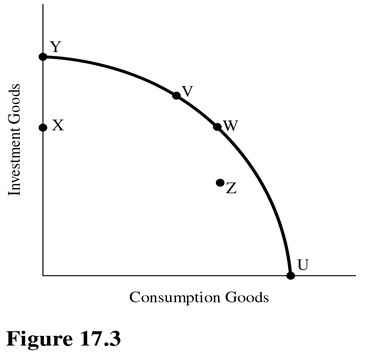
 Refer to Figure 17.3. Assume X units of plants and equipment wear out each year. What will happen to the PPC in the future if the economy currently produces at point W?
Refer to Figure 17.3. Assume X units of plants and equipment wear out each year. What will happen to the PPC in the future if the economy currently produces at point W?
A. It will shift outward.
B. It will shift inward.
C. It will stay roughly the same.
D. This cannot be determined with the information given.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Refer to Horizontal Merger. As a consequence of the merger, consumers lose surplus equal to
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the effects of a horizontal merger. Before the merger, the firm behaves competitively producing Q0 and charging P0. The merger lowers the firm's marginal cost and gives the firm enough market power to switch to the monopoly equilibrium.
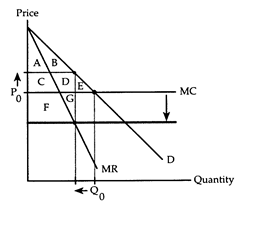
a. Area A + B.
b. Area C + D.
c. Area C + D + E.
d. Area G.
Purchasing power parity (PPP) measurements of income are a way to make international comparisons by correcting for national differences in
A) unemployment. B) inflation. C) prices of goods and services. D) economic growth. E) government subsidies.
Most economists agree that the best rate of inflation for a stable economy would be around:
A. zero. B. two to three percent. C. five to six percent. D. seven percent.
Assume that currently one U.S. dollar will purchase £0.65. Investors believe that one year from now a U.S. dollar will purchase £0.72. If we consider the U.S. dollar-pound market, where the horizontal axis measure the quantity of pounds, explain what we are likely to see in terms of demand and supply and the exchange rate.
What will be an ideal response?