How is the chemiosmotic process shown in the figure similar to secondary active transport (cotransport) of solutes (discussed in Chapter 3)?
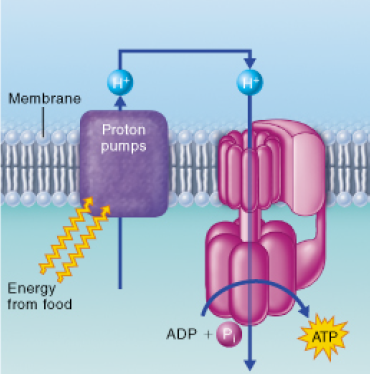
a. Both processes are powered by an electron transport chain, which transports ions across a membrane.
b. Both processes use an electrochemical gradient to store energy.
c. Both processes result in the synthesis of ATP.
d. Both processes typically involve H+ (proton) gradients.
b. Both processes use an electrochemical gradient to store energy.
During electron transport, energy is stored in the form of a proton gradient. H+ ions’ diffusion back across the
membrane releases this energy and powers ATP synthesis. Secondary active transport uses the energy released by
diffusion of ions such as sodium to power the cotransport of other solute molecules, such as glucose
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1. All enzymes are proteins. 2. Because of the abundance of ribosomes, translation is NOT an energy costly process for the cell. 3. The cells of every organism make only a few different tRNA molecules encoded by the same gene. 4. In eukaryotes, 40S and 60S combine to form a 100S ribosome.
Biodiversity encompasses various levels of organization. Select the exception
a. genetic variation b. species richness c. interactions among ecosystems d. diversity of different ecosystems e. interactions between biomes
Development of the human embryo's heart begins in the ________ week.
A. 16th B. 6th C. 1st D. 3rd E. 24th
Respond to the following statements with reference to the five trophic categories listed below.
A. B. A herbivore is this. C. A bear eating blueberries is functioning as this. D. A Venus flytrap devouring an insect to obtain nitrogen functions as this. E. A bear feeding on an adult salmon (which eats other fish, squid, and shrimp) is functioning as this. F. Most fungi function as this.