The result of a hypothesis is described in terms of the probability of obtaining a particular sample. Use the given context to formulate the null and alternative hypotheses. Discuss whether the sample provides evidence for rejecting the null hypothesis.A company claims that the proportion of defectives among its new DVD players is only 0.01 (1%). A consumer group believes that the proportion of defectives is higher than this. The consumer group picks a random sample of 200 of the DVD players and finds the proportion of defectives in the sample to be 0.022. Assuming that the proportion of defectives for all the company's DVD players is p = 0.01, the probability of selecting a sample in which the proportion of defectives is 0.022 or more is 0.044.
What will be an ideal response?
Null hypothesis: proportion of defective DVD players = 0.01
Alternative hypothesis: proportion of defective DVD players > 0.01
Result is significant at the 0.05 level, and provides evidence for rejecting the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis that the proportion of defectives is greater than 0.01.
You might also like to view...
Integrate the function.
A. 2tan-1 
B. 2tan-1 5
C. 2sin-1 5
D. 
Four players (A, B, C, and D) agree to divide the 15 items shown below by lining them up in order and using the method of markers. The players' bids are as indicated.
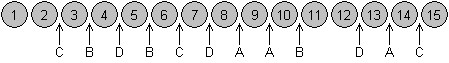 Item 13
Item 13
A. goes to A. B. goes to B. C. goes to C. D. goes to D. E. is left over.
a. Find an equation of the sphere that passes through the point (6,-5,3) and has center (-3,5,3). b. Find the curve in which this sphere intersects the xy-plane.
What will be an ideal response?
Simplify.(-2x3)4
A. 16x12 B. -16x7 C. -16x12 D. 16x7