The most frequent cause of uncomplicated community-acquired urinary tract infections is:
a. S. saprophyticus.
b. Klebsiella spp.
c. E. coli.
d. Proteus.
C
E. coli is the most frequently isolated agent of uncomplicated community-acquired urinary tract infections.
You might also like to view...
The three phylogenetic trees above all contain the same members, all have a common ancestor, but are divided up in three different ways. Which tree has members circled that are of several evolutionary lines and does not include the most recent common ancestor of the included lineages? What is this type of group is this?
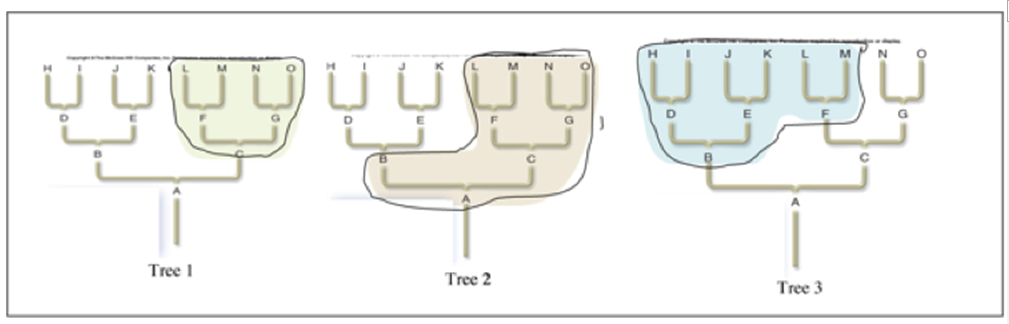
A. Tree 3; polyphyletic.
B. Tree 2; polyphyletic.
C. Tree 1; monophyletic.
D. Tree 3; monophyletic.
E. Tree 2; paraphyletic.
During the initiation of translation, the small ribosomal subunit binds mRNA, and then the initiator tRNA base-pairs with mRNA. Which step happens next?
a. The ribosome catalyzes the formation of the first peptide bond. b. The first tRNA is released. c. The large ribosomal subunit joins the small subunit. d. The ribosome starts the assembly of the amino acid chain. e. The second tRNA base-pairs with the mRNA.
The ________ zone extends from a depth of 200 to 4000 meters.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
A base at the first position of an anticodon on the tRNA would pair with a base at the ________ position of the mRNA
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word