Triton, the largest of Neptune's moons has a retrograde rotation. This means that it revolves about Neptune in the opposite direction to Neptune's direction of rotation about its own axis
The gravitational attraction of Triton causes tides on Neptune, which gradually slow down its rotation about its own axis. What consequences does this have for Triton?
Since the angular momentum of the Neptune-Triton system has to be conserved, a decrease in the angular momentum of Neptune about its axis must be balanced by an increase of Triton's angular momentum about that axis. But since Triton is orbiting Neptune in the opposite direction, its angular momentum will actually decrease. Triton's orbit will thus gradually decay until it either breaks up or falls into Neptune.
You might also like to view...
Intensity: Which one of the following expressions is the correct representation for the speed of light in vacuum?
A. 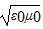
B. 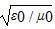
C. 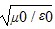
D. 1 / 
E. 1 / ?0?0
The stars with masses comparable to our Sun's, but sizes like the Earth are
A) red giants. B) red main sequence stars. C) neutron stars. D) white dwarfs. E) blue main sequence stars.
To be able to do work, a system must have _______
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
The planet that rotates on its side is
• •(a) Earth •(b) Jupiter •(c) Mars •(d) Uranus