Topic 2.13 - Microbial Symbioses
What will be an ideal response?
•What types of interactions are considered symbioses?
•What kinds of effects do symbionts have on their hosts?
•How do environmental factors affect symbiotic outcomes?
•What happens in cases where more than one symbiont is present?
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure above. What is the function of the ACC sequence at the end?
A) It attaches to an amino acid. B) It base pairs with the codon of mRNA. C) It stabilizes the tRNA-amino acid complex. D) It is the active site of this ribozyme.
You have been studying the effect of a concentration gradient on the rate of transport of a nutrient into a bacterial cell. If a carrier protein is involved in the transport of this nutrient, which curve would you expect to see?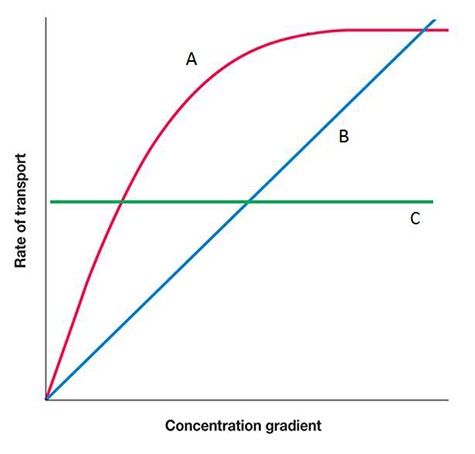
A. B B. A C. C
Which phase of cellular respiration produces the most ATP?
a. the Krebs cycle b. electron transfer phosphorylation c. glycolysis d. all of the phases are equally productive
In a strawberry plant in the summer, the leaves are ________ and the strawberry fruits are ________
A) sugar sources… sugar sources B) sugar sources… sugar sinks C) sugar sinks… sugar sources D) sugar sinks… sugar sinks