The individual pictured in Figure 5.3
A) must be risk-averse.
B) must be risk-neutral.
C) must be risk-loving.
D) could be risk-averse, risk-neutral, or risk-loving.
E) could be risk-averse or risk-loving, but not risk-neutral.
C
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a decrease in government spending that decreases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD will lead to a short-run equilibrium at__ creating _____gap.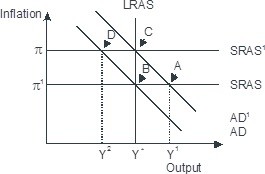
A. B; no output B. D; an expansionary C. B; recessionary D. D; a recessionary
Public parks and libraries are examples of
a. economic goods. b. free goods. c. intangible goods. d. public goods.
When oligopolists join together in a cartel, they: a. choose to ignore their mutual interdependence
b. indicate awareness that their behavior is interdependent. c. violate the law of supply and demand. d. attempt to behave like perfect competitors.
A profit-maximizing monopolist
A. is just as socially efficient as a perfectly competitive firm in allocating resources to production since he or she, too, seeks the largest return on his or her investment. B. produces an output level at which marginal utility exceeds marginal cost. C. produces more output than a perfectly competitive industry. D. always produces in the inelastic region of his or her demand curve.