The wire in Fig. 29-2 carries a current I that is decreasing with time at a constant rate. The induced emf in each of the loops is such that
A)
no emf is induced in any loop.
B)
all loops experience counterclockwise emf.
C)
loop A has clockwise emf, loop B has no induced emf, and loop C has counterclockwise emf.
D)
loop A has counterclockwise emf, loop B has no induced emf, and loop C has clockwise emf.
E)
loop A has counterclockwise emf, loop B clockwise emf, and loop C has clockwise emf.
D
You might also like to view...
Which of these expands when the temperature is lowered?
A) iron B) wood C) ice water D) helium E) none of the above
The circuit below shows three resistors in parallel. R3 > R2 > R1. The resistors are all made of the same wire with the same diameter but have different lengths. Rank the magnitudes of the electric fields in the resistors from least to greatest
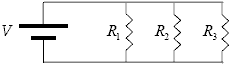
a.
E3 < E2 < E1.
b.
E2 < E1 = E3.
c.
E1 = E2 = E3.
d.
E1 = E3 < E2.
e.
E1 < E2 < E3.
What two physical processes balance each other to create the condition known as gravitational equilibrium in stars?
A) the strong force and the weak force B) gravitational force and outward pressure C) gravitational force and surface tension D) the strong force and the electromagnetic force
Which has the more predictable behavior, an electron or a proton, and why?
A) An electron, because of its smaller mass. B) A proton, because of its larger mass. C) A proton, because it does feel the nuclear force. D) An electron, because of its smaller charge. E) An electron, because it doesn't feel the nuclear force.