In the lab, you choose to design a simple experiment to distinguish between hydrophilic and hydrophobic substances. You start by adding equal amounts of vinegar and oil to a container
After shaking, the vinegar and oil levels separate, based upon polarity and density. To this you add glucose and sodium citrate and shake again. Where do you expect to find the glucose and sodium citrate in greatest quantities?
A) Both will concentrate in the oil layer.
B) The glucose will concentrate in the vinegar, sodium citrate in the oil.
C) Both will concentrate in the vinegar layer.
D) Sodium citrate will concentrate in the vinegar, glucose in the oil.
E) Both will be uniform throughout both layers.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Many organisms used in modern agriculture are a result of artificial selection
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Two bacterial genes are transduced simultaneously. What does this suggest about their proximity to each other within the original host genome?
A. Not a thing-it's highly likely that two separate virus particles were carrying each gene, and that they coinfected the new target cell at the same time, delivering their genetic payloads. This could mean the two original genes might not even be from the same original host cell! B. It's highly likely that the two genes are located next to each other in the original host cell chromosome. Since transduction relies on either mispackaging of bits of host cell DNA into non-functional virus units, or improper excision of lysogenic phage DNA from a host cell chromosome (carrying parts of the host cell DNA with it), the genes must lie close to each other to be transduced into a new cell simultaneously. C. They must be within five gene lengths of each other, but not necessarily immediately adjacent. If they were immediately adjacent, the transposons that facilitate the transfer of genetic information between the two cells wouldn't be able to 'jump' into them. D. It doesn't mean anything. Transduction relies on the ability of a cell to take up foreign DNA. It's possible here that the cell has simply taken up two separate bits of DNA at the same time from the surrounding environment.
Calculate L1, given n1 = 100, n2 = 50, and n3 = 10
A) 90 B) 50 C) 75 D) 10
Match the terms with the labeled structures on the diagram. 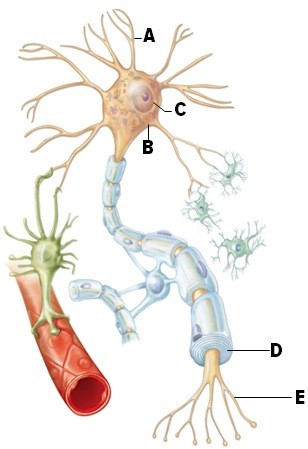 axon
axon
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).