Public goods are
A. rival in consumption, and their benefits are nonexcludable.
B. rival in consumption, and their benefits are excludable.
C. nonrival in consumption, and their benefits are excludable.
D. nonrival in consumption, and their benefits are nonexcludable.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
By fixing its exchange rate, China is most likely
A) achieving a low inflation rate by anchoring to the U.S. inflation rate. B) keeping its export prices low. C) making it easier to compete in world markets. D) Both B and C.
A decrease in the market clearing exchange value of the home nation's currency in terms of the currency of another nation is a home currency
A) appreciation. B) revaluation. C) depreciation. D) devaluation.
Which of the following is a result of the health care reform enacted in 2010? a. Everyone in the U.S. must purchase health-care coverage or pay a fine
b. Every firm with more than 50 employees must offer health-care coverage. c. Health insurance companies must cover everyone that applies regardless of preexisting conditions. d. all of the above
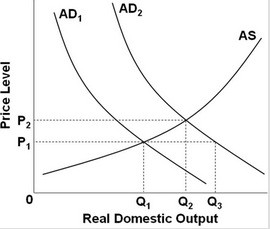 Refer to the above diagram. A shift from AD1 to AD2 would be consistent with what economic event in U.S. history?
Refer to the above diagram. A shift from AD1 to AD2 would be consistent with what economic event in U.S. history?
A. Full-employment in the late 1990s. B. Cost-push inflation in the mid-1970s. C. Demand-pull inflation in the late 1960s. D. Recession in 2001.