Scattered fibroblasts amid loosely arranged collagenous and elastic fibers.
What will be an ideal response?
Areolar connective tissue
You might also like to view...
Active -galactosidase enzyme is observed only in E. coli growing in the presence of lactose. One hypothesis is that the enzyme is always being produced, but is produced in an unstable form that breaks down rapidly in the absence of lactose (hypothesis 1)
A second hypothesis is that the enzyme is stable, but is produced only in the presence of lactose (hypothesis 2). An experiment was performed to test these hypotheses. A culture of growing cells was exposed to lactose, which was later removed. The amount of -galactosidase present in the culture during the course of the experiment was measured. The data are shown in the graph below. Which one of the following statements is a conclusion that can be obtained from these experimental data? A. The amount of -galactosidase in the culture decreased rapidly after lactose was removed, in support of hypothesis 2. B. The amount of -galactosidase in the culture decreased rapidly after lactose was removed, in support of hypothesis 1. C. The amount of -galactosidase in the culture remained stable after lactose was removed, in support of hypothesis 1. D. Synthesis of -galactosidase is turned on when lactose is added and turned off when lactose is removed, in support of hypothesis 2. E. Synthesis of -galactosidase is turned on when lactose is added and turned off when lactose is removed, in support of hypothesis 1.
When are the oocytes formed in a human female?
a. When she is pre-adolescent b. Each month as part of the menstrual cycle c. During puberty d. During her own embryonic development
Identify the labeled structures on the human skeleton in the picture. 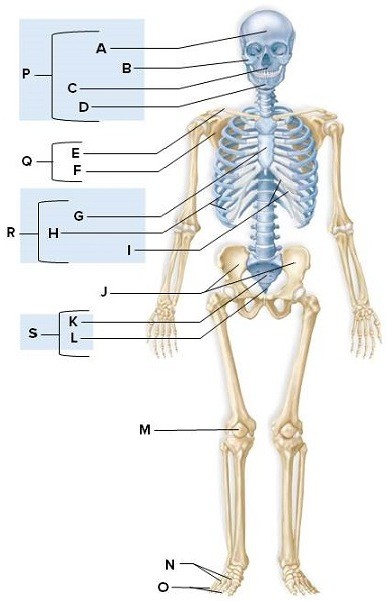 A: ________B: ________C: ________D: ________E: ________F: ________G: ________H: ________I: ________J: ________K: ________L: ________M: ________N: ________O: ________P: ________Q: ________R: ________S: ________
A: ________B: ________C: ________D: ________E: ________F: ________G: ________H: ________I: ________J: ________K: ________L: ________M: ________N: ________O: ________P: ________Q: ________R: ________S: ________
What will be an ideal response?
What happens to glutamic acid 35 and aspartic acid 52 at the end of the reaction?
A.) both amino acids are restored to their original forms B.) glutamic acid is deprotonated and negatively charged C.) lysozyme is destroyed and recycled as the product is released D.) aspartic acid has formed a covalent bond with the first sugar